Outcomes of transitioning from mandatory to elective research at a dental school in Southern California
- PMID: 39533530
- PMCID: PMC12174485
- DOI: 10.1002/jdd.13770
Outcomes of transitioning from mandatory to elective research at a dental school in Southern California
Abstract
Objectives: The purpose of this study was to assess the impact of a curricular change from mandatory to elective research on the student research outcomes at a Southern California Dental School over ten years. Additionally, the perception of dental students and faculty toward research in dental education was assessed.
Methods: A survey was distributed to determine the perception towards research in dental education, motivation and barriers for pursuing research and the possibility participants would pursue research-even if the school did not mandate it. The survey was distributed to a total of 507 dental students and 121 full-time faculty.
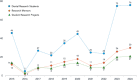
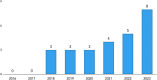
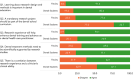
Results: Both dental students (80.6%) and faculty (91.4%) agreed that learning about research is important in dental education. Both cohorts generally agreed that research experience enhances dental training, supports the scientific basis of dental treatment methods, and correlates with clinical ability. The majority of students (77.0%) disagreed with mandating research while faculty (77.6%) believed that it should be mandated. Lack of time was the single most stated barrier for participating in research. The overall trend during the transition from mandatory to elective research showed that initially there was a stark drop in students and faculty participation and projects being carried out. However, with deliberate planning, research outcomes steadily increased.
Conclusions: We conclude that dental students and faculty have a positive perspective on the importance of research in dental education and actively engage in research and mentoring activities when provided with a supportive and encouraging environment. This participation occurs regardless of whether research is mandated or elective.
Keywords: dental education; faculty; perception; research; students.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Dental Education published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Dental Education Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative analysis of layered curriculum and project-based learning approaches in an oral radiological course.J Dent Educ. 2025 Jun;89(6):813-822. doi: 10.1002/jdd.13775. Epub 2024 Nov 14. J Dent Educ. 2025. PMID: 39543831 Clinical Trial.
-
Dental Students' Attitudes Toward Tobacco Cessation in the Dental Setting: A Systematic Review.J Dent Educ. 2017 May;81(5):500-516. doi: 10.21815/JDE.016.016. J Dent Educ. 2017. PMID: 28461627
-
Student, Staff and Faculty Experience with a Medical School Racial and Sociopolitical Trauma Protocol: A Mixed Methods Study.Teach Learn Med. 2025 Jun-Jul;37(3):375-387. doi: 10.1080/10401334.2024.2361912. Epub 2024 Jun 7. Teach Learn Med. 2025. PMID: 38847650
-
Transforming dental education: interactive and student-centered learning with team-based learning in the undergraduate program.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 3;12:1579237. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1579237. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40529146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Readiness to use artificial intelligence: a comparative study among dental faculty members and students.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Jul 4;25(1):1006. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07621-w. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40615869 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Commission of Dental Accreditation . Accreditation Standards for Dental Education Programs. American Dental Association; 2016.
-
- Polverini PJ. Why integrating research and scholarship into dental education matters. J Dent Educ. 2014;78(3):332‐333. - PubMed
-
- Bertolami CN. The role and importance of research and scholarship in dental education and practice. J Dent Educ. 2002;66(8):918‐924. discussion 925‐6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources