Effect of muscle strength on deep vein thrombosis: A Mendelian randomization study
- PMID: 39533595
- PMCID: PMC11557092
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000040138
Effect of muscle strength on deep vein thrombosis: A Mendelian randomization study
Abstract
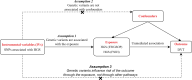
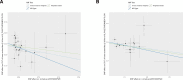
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition characterized by blood clots in deep veins, posing a significant public health burden. Muscle strength has been implicated as a potential risk factor for DVT due to its influence on venous return. This study aims to investigate the causal association between muscle strength and DVT using a Mendelian randomization (MR) approach, leveraging genetic variants as instrumental variables (IVs). We conducted a 2-sample MR analysis using genome-wide association study (GWAS) data for hand-grip strength and DVT. IVs were selected based on their significant associations with muscle strength and DVT, as well as their linkage disequilibrium patterns. We employed statistical methods including inverse-variance weighting (IVW), MR-Egger, and weighted median to address pleiotropy bias. Sensitivity analyses were conducted to evaluate the robustness of the results. A total of 21 and 14 independent IVs were identified for hand grip strength (EWGSOP) and hand grip strength (FNIH), respectively. IVW analysis revealed a consistent causal and negative association between both definitions of hand grip strength and DVT (EWGSOP: OR = 0.702, 95% CI: 0.511-0.964, P = .029; FNIH: OR = 0.715, 95% CI: 0.570-0.898, P = .004). No directional pleiotropy was detected in MR-Egger and MR-PRESSO analyses for either definition (EWGSOP: MR-Egger Intercept P = .516; MR-PRESSO global test P = .162; FNIH: MR-Egger Intercept P = .569; MR-PRESSO global test P = .371).Sensitivity analyses demonstrated the stability of the causal effect estimates, with little influence from individual IVs. The MR analysis provided evidence of a causal association between muscle strength and DVT risk, suggesting that increasing muscle strength may have a protective effect. These findings have implications for preventive strategies and the promotion of resistance exercises and muscle-strengthening activities. Further research and validation of these results could inform clinical guidelines and interventions for DVT prevention.
Copyright © 2024 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Associations between deep venous thrombosis and thyroid diseases: a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jun 14;29(1):327. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01933-1. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38877527 Free PMC article.
-
A Mendelian randomization study revealed a causal link between napping and deep vein thrombosis (DVT).Sleep Breath. 2024 May;28(2):665-671. doi: 10.1007/s11325-023-02940-y. Epub 2023 Oct 26. Sleep Breath. 2024. PMID: 37884785
-
The genetic causal relationship between type 2 diabetes, glycemic traits and venous thromboembolism, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Thromb J. 2024 Mar 29;22(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12959-024-00600-z. Thromb J. 2024. PMID: 38553747 Free PMC article.
-
Caffeinated beverages intake and risk of deep vein thrombosis: A Mendelian randomization study.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 13;19(2):e0298123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298123. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38349931 Free PMC article.
-
[Genetic Causation Analysis of Hyperandrogenemia Testing Indicators and Preeclampsia].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 May 20;55(3):566-573. doi: 10.12182/20240560106. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 38948277 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Memtsoudis SG, Della Valle AG, Besculides MC, Esposito M, Koulouvaris P, Salvati EA. Risk factors for perioperative mortality after lower extremity arthroplasty: a population-based study of 6,901,324 patient discharges. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25:19–26. - PubMed
-
- Naess IA, Christiansen SC, Romundstad P, Cannegieter SC, Rosendaal FR, Hammerstrøm J. Incidence and mortality of venous thrombosis: a population-based study. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5:692–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

