Self-Management and Its Associated Factors Among People Living With HIV at University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 39534103
- PMCID: PMC11557183
- DOI: 10.1155/2024/5590331
Self-Management and Its Associated Factors Among People Living With HIV at University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
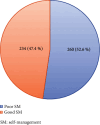
Background: Self-management (SM) is the gold standard of care and is the direct active participation of patients in their disease management. Condition-specific factors, physical and social environment, individual and family, and the process of SM are factors that influence SM in people living with human immunodeficiency virus (PLHIV). Poor SM leads to high retroviral infection transmission, mortality, and morbidity. Objective: This study was aimed at assessing SM and its associated factors among PLHIV at the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital (UOGCSH), Northwest Ethiopia. Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted using a systematic random sampling technique at the UOGCSH from May 20 to July 30, 2022. The data were collected using a previously validated tool and were entered and analyzed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences Version 25. A binary logistic regression analysis was used to identify factors associated with poor SM. The statistical significance was considered at a p value < 0.05. Result: Of 419 PLHIV, the median (IQR) SM score was 39 (9), and above half (52.6%, 95% CI: 48%-57%) of them had poor SM. Being unemployed (AOR = 2.49, 95%CI = 1.19, 5.19), living alone (AOR = 2.16, 95%CI = 1.12, 4.17), unfamiliar with the management of HIV-related symptoms (AOR = 3.59, 95%CI = 2.08, 6.20), poor social support (AOR = 3.02, 95%CI = 1.54, 5.93), poor self-efficacy (AOR = 3.04, 95%CI = 1.83, 5.06), and unsupported by the adherence support group (AOR = 17.17, 95%CI = 8.37, 35.22) were significantly associated with poor SM. Conclusion: The majority of PLHIV had poor SM. This study supports the findings of individual family SM theory and previously published studies regarding factors affecting SM. The government, hospital, adherence support groups, and PLHIV should work on modifiable sociodemographic, condition-specific, and process of SM to improve SM of PLHIV.
Keywords: HIV/AIDS; people living with HIV; process of self-management; self-management.
Copyright © 2024 Abdisa Gemedi Jara et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Self-efficacy of PLHIV for self-management at the University of Gondar Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.BMC Prim Care. 2024 Jul 15;25(1):255. doi: 10.1186/s12875-024-02502-5. BMC Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 39009959 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of alcohol use disorder on antiretroviral therapy adherence in adults with HIV/AIDS at University of Gondar, Northwest Ethiopia.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 29;14(1):29745. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79406-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39613796 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive foot self-care practice and associated factors among diabetic patients attending the university of Gondar comprehensive specialized referral hospital, Northwest Ethiopia, 2021.BMC Endocr Disord. 2022 May 11;22(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s12902-022-01044-0. BMC Endocr Disord. 2022. PMID: 35546665 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of sleep and associated factors among people living with HIV/AIDS attending ART clinic at Hawassa University comprehensive specialized Hospital, Hawassa, SNNPR, Ethiopia.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 4;15(6):e0233849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233849. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32497153 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary diversity and associated factors among HIV-positive adults attending the anti-retroviral therapy clinic at Felege Hiwot Comprehensive Specialized Hospital, Northwest Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study.J Nutr Sci. 2021 Mar 11;10:e18. doi: 10.1017/jns.2021.5. eCollection 2021. J Nutr Sci. 2021. PMID: 33889401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- UNAIDS. FACT SHEET on GLOBAL HIV statistics: ending the AIDS epidemic UNAIDS . UNAIDS; 2022.
-
- Creer T. L., Renne C. M., Christian W. P. Behavioral contributions to rehabilitation and childhood asthma. Rehabilitation Literature . 1976;37(8):226–32,247. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical