Autistic features in patients with intellectual disability attending the psychiatry outpatient department of a tertiary healthcare center
- PMID: 39534158
- PMCID: PMC11553612
- DOI: 10.4103/ipj.ipj_128_24
Autistic features in patients with intellectual disability attending the psychiatry outpatient department of a tertiary healthcare center
Abstract
Background: Meta-syndromic groups with cognitive and relational impairment include both autism spectrum disorder (ASD) and intellectual disability (ID). When it comes to individuals with intellectual difficulties, autistic traits are often unexplored unless they reach the level of the syndrome. The presence of both autism and ID increases disability percentage.
Aim: To study the presence of autistic symptoms in individuals with ID.
Materials and methods: This was a cross-sectional, observational study in which after informed consent from caretakers of patients with ID, clinical history and sociodemographic details were recorded. Further Indian Scale for Assessment of Autism (ISAA) was administered for evaluation of autistic features. Statistical analysis of the data was done using the Chi-square test and Spearman's correlation.
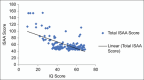
Results: Out of 150 subjects with ID, 18% (n = 27) were diagnosed with comorbid ASD. A statistically significant (P value = <0.001) association was found between the severity of ID (intelligence quotient, [IQ]) and the severity of autism in patients. Various domains of autism like social relation and reciprocity, speech, language, communication, emotional responsiveness, etc., showed a statistically significant correlation with IQ.
Conclusion: This study finding also highlights that lower IQ scores, i.e., severe ID have higher incidence and severity of autistic features. Improving assessment both clinically and on objective testing can help in planning rehabilitation for these patients.
Keywords: Autism; Indian scale for assessment of autism; autism spectrum disorder; intellectual disability.
Copyright: © 2024 Industrial Psychiatry Journal.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Empathizing, systemizing, empathizing-systemizing difference and their association with autistic traits in children with autism spectrum disorder, with and without intellectual disability.Autism Res. 2022 Jul;15(7):1348-1357. doi: 10.1002/aur.2766. Epub 2022 Jun 19. Autism Res. 2022. PMID: 35719032
-
The effect of epilepsy on autistic symptom severity assessed by the social responsiveness scale in children with autism spectrum disorder.Behav Brain Funct. 2016 Jun 27;12(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s12993-016-0105-0. Behav Brain Funct. 2016. PMID: 27350381 Free PMC article.
-
Epilepsy and Autism Severity: A Study of 6,975 Children.Autism Res. 2019 Aug;12(8):1251-1259. doi: 10.1002/aur.2132. Epub 2019 May 24. Autism Res. 2019. PMID: 31124277
-
Intellectual functioning and behavior in Dravet syndrome: A systematic review.Epilepsy Behav. 2020 Jul;108:107079. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2020.107079. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Epilepsy Behav. 2020. PMID: 32334365
-
Vision Research Literature May Not Represent the Full Intellectual Range of Autism Spectrum Disorder.Front Hum Neurosci. 2017 Feb 14;11:57. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00057. eCollection 2017. Front Hum Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28261072 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1992. The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines.
-
- Maulik PK, Mascarenhas MN, Mathers CD, Dua T, Saxena S. Prevalence of intellectual disability: A meta-analysis of population-based studies. Res Dev Disabil. 2011;32:419–36.. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources