Perspectives of Caregivers on Access to Health Care for Children with CKD
- PMID: 39534191
- PMCID: PMC11551112
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.08.029
Perspectives of Caregivers on Access to Health Care for Children with CKD
Abstract
Introduction: Inequitable access to health care based on demographic factors such as ethnicity, socioeconomic status and geographical location has been consistently found in children with chronic kidney disease (CKD). However, little is known about the perspectives of caregivers on accessing health care. We described caregivers' perspectives on accessing health care for children with CKD from socioeconomically disadvantaged backgrounds and/or rural or remote areas.
Methods: Caregivers of Australian children aged 0 to 16 years, across all CKD stages, from low socioeconomic status backgrounds, and/or residing in rural or remote areas, purposively sampled from 5 centers, participated in semi structured interviews on accessing health care. Transcripts were analyzed thematically.
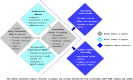
Results: From 32 interviews, we identified 6 themes: lack of agency undermining ability to seek care (obscurity of symptoms, uncertain and confused about care processes, and vulnerable and unable to advocate), losing trust in clinicians (confused by inconsistencies and ambiguities in advice, and distressed by lack of collaborative care), exasperated by organizational rigidity (frustrated by bureaucratic roadblocks, lack of access to specialist care in rural and remote settings, and inadequacies of support programs), compounding burden of caregiving (unsustainable financial pressure, debilitating exhaustion, and asymmetry of responsibility), intensifying strain on family (uprooting to relocate, sibling stress and neglect, and depending on family support), building resilience and stability (empowerment through education and confidence in technical and medical support).
Conclusions: Caregivers of children with CKD from disadvantaged backgrounds feel disempowered and vulnerable when accessing care for their child. Strategies are needed to improve access to health care for families who are socioeconomically or geographically disadvantaged.
Keywords: access; caregivers; chronic kidney disease; healthcare; pediatric.
© 2024 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Australian Rural Caregivers' Experiences in Supporting Patients With Kidney Failure to Access Dialysis and Kidney Transplantation: A Qualitative Study.Am J Kidney Dis. 2022 Dec;80(6):773-782.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2022.05.015. Epub 2022 Jul 20. Am J Kidney Dis. 2022. PMID: 35868538
-
Parental perspectives on the financial impact of caring for a child with CKD.Am J Kidney Dis. 2015 Mar;65(3):384-93. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.07.019. Epub 2014 Sep 20. Am J Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 25245301
-
Child and caregiver perspectives on access to psychosocial and educational support in pediatric chronic kidney disease: a focus group study.Pediatr Nephrol. 2023 Jan;38(1):249-260. doi: 10.1007/s00467-022-05551-z. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Pediatr Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 35471462
-
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Patients With CKD: Systematic Review of Qualitative Studies.Am J Kidney Dis. 2023 Oct;82(4):395-409.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2023.04.001. Epub 2023 Jun 16. Am J Kidney Dis. 2023. PMID: 37330133 Free PMC article.
-
Patients' and caregivers' perspectives on access to kidney replacement therapy in rural communities: systematic review of qualitative studies.BMJ Open. 2020 Sep 23;10(9):e037529. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-037529. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32967878 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources