TRPC6-Calpain-1 Axis Promotes Tubulointerstitial Inflammation by Inhibiting Mitophagy in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 39534194
- PMCID: PMC11551102
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.08.019
TRPC6-Calpain-1 Axis Promotes Tubulointerstitial Inflammation by Inhibiting Mitophagy in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Introduction: Renal tubulointerstitial inflammation represents an effective indicator for predicting the progression of diabetic kidney disease (DKD). Mitophagy abnormality is 1 of the most important factors involved in tubule injury. However, the exact molecular mechanism underlying mitophagy abnormality-mediated tubulointerstitial inflammation in DKD remains poorly understood.
Methods: In this study, a streptozotocin-induced DKD mouse model was established and HK-2 cells treated with high glucose (HG) served as an in vitro model. Tubular mitophagy was regulated through pharmacological urolithin A (UA) administration. The functional effect of the transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily C, member 6 (TRPC6) was explored using genetic interventions in vivo and in vitro.
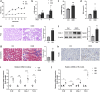
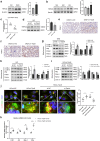
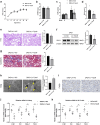
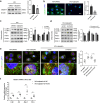
Results: We found that renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in DKD was closely associated with mitophagy inhibition, which was mediated by disturbance of PINK1/Parkin pathway. Mitophagy activation significantly attenuated tubular injury and tubulointerstitial inflammation. Further, it was found that TRPC6 was markedly increased in DKD and played an essential role in mitophagy inhibition by activating calpain-1. Knockdown of Trpc6 partially reversed mitophagy abnormality and consequently attenuated tubular injury and tubulointerstitial inflammation in vivo and in vitro. Finally, we found that tubular TRPC6-mediated mitophagy inhibition was blocked with BAPTA (a specific Ca2+ chelator) or calpeptin (a specific calpain-1 inhibitor).
Conclusion: Our study reveals that TRPC6-calpain-1 axis promotes tubulointerstitial inflammation in DKD by inhibiting mitophagy.
Keywords: TRPC6; calpain-1; diabetic kidney disease; mitophagy; tubulointerstitial inflammation.
© 2024 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Huangkui capsule attenuates diabetic kidney disease through the induction of mitophagy mediated by STING1/PINK1 signaling in tubular cells.Phytomedicine. 2023 Oct;119:154975. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154975. Epub 2023 Jul 18. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37517171
-
Podocyte Injury in Diabetic Kidney Disease in Mouse Models Involves TRPC6-mediated Calpain Activation Impairing Autophagy.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023 Nov 1;34(11):1823-1842. doi: 10.1681/ASN.0000000000000212. Epub 2023 Sep 6. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 37678257 Free PMC article.
-
Tacrolimus ameliorates tubulointerstitial inflammation in diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting the NFATc1/TRPC6 pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Sep;24(17):9810-9824. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15562. Epub 2020 Aug 11. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32779844 Free PMC article.
-
Role of TRPC6 in Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2019 May 21;21(7):48. doi: 10.1007/s11906-019-0960-9. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2019. PMID: 31115705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in understanding and treating diabetic kidney disease: focus on tubulointerstitial inflammation mechanisms.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 4;14:1232790. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1232790. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37859992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural small molecules regulating the mitophagy pathway counteract the pathogenesis of diabetes and chronic complications.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1571767. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1571767. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40308774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Understanding of Mitochondrial Function in Diabetic Kidney Disease.Kidney Int Rep. 2024 Dec 5;10(2):285-286. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.12.001. eCollection 2025 Feb. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 39990914 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Mitochondrial quality control in diabetes mellitus and complications: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Aug 27;16(1):652. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07936-y. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40866350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of mitophagy-related biomarkers in severe acute pancreatitis: integration of WGCNA, machine learning algorithms and scRNA-seq.Front Immunol. 2025 May 28;16:1594085. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1594085. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40503237 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jiang W.J., Xu C.T., Du C.L., et al. Tubular epithelial cell-to-macrophage communication forms a negative feedback loop via extracellular vesicle transfer to promote renal inflammation and apoptosis in diabetic nephropathy. Theranostics. 2022;12:324–339. doi: 10.7150/thno.63735. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

