Artificial intelligence assisted common maternal fetal planes prediction from ultrasound images based on information fusion of customized convolutional neural networks
- PMID: 39534222
- PMCID: PMC11554532
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1486995
Artificial intelligence assisted common maternal fetal planes prediction from ultrasound images based on information fusion of customized convolutional neural networks
Abstract
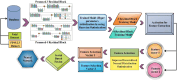
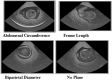
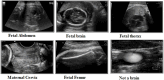
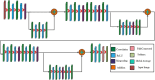
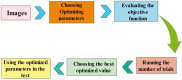
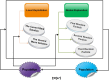
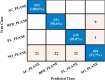
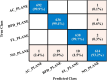
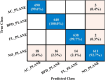
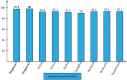
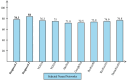
Ultrasound imaging is frequently employed to aid with fetal development. It benefits from being real-time, inexpensive, non-intrusive, and simple. Artificial intelligence is becoming increasingly significant in medical imaging and can assist in resolving many problems related to the classification of fetal organs. Processing fetal ultrasound (US) images increasingly uses deep learning (DL) techniques. This paper aims to assess the development of existing DL classification systems for use in a real maternal-fetal healthcare setting. This experimental process has employed two publicly available datasets, such as FPSU23 Dataset and Fetal Imaging. Two novel deep learning architectures have been designed in the proposed architecture based on 3-residual and 4-residual blocks with different convolutional filter sizes. The hyperparameters of the proposed architectures were initialized through Bayesian Optimization. Following the training process, deep features were extracted from the average pooling layers of both models. In a subsequent step, the features from both models were optimized using an improved version of the Generalized Normal Distribution Optimizer (GNDO). Finally, neural networks are used to classify the fused optimized features of both models, which were first combined using a new fusion technique. The best classification scores, 98.5 and 88.6% accuracy, were obtained after multiple steps of analysis. Additionally, a comparison with existing state-of-the-art methods revealed a notable improvement in the suggested architecture's accuracy.
Keywords: deep learning; information fusion; maternal fetal; optimization; residual blocks; ultrasound.
Copyright © 2024 Rauf, Attique Khan, Albarakati, Jabeen, Alsenan, Hamza, Teng and Nam.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
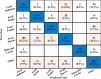
Figures
Similar articles
-
Automated deep bottleneck residual 82-layered architecture with Bayesian optimization for the classification of brain and common maternal fetal ultrasound planes.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Dec 20;10:1330218. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1330218. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 38188327 Free PMC article.
-
SkinNet-INIO: Multiclass Skin Lesion Localization and Classification Using Fusion-Assisted Deep Neural Networks and Improved Nature-Inspired Optimization Algorithm.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Sep 6;13(18):2869. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13182869. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37761236 Free PMC article.
-
Novel neural network classification of maternal fetal ultrasound planes through optimized feature selection.BMC Med Imaging. 2024 Dec 18;24(1):337. doi: 10.1186/s12880-024-01453-8. BMC Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39696025 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial intelligence in clinical care amidst COVID-19 pandemic: A systematic review.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021;19:2833-2850. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.05.010. Epub 2021 May 7. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34025952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deep learning for colon cancer histopathological images analysis.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Sep;136:104730. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104730. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34375901 Review.
Cited by
-
A review on computer-aided diagnostic system to classify the disorders of the gastrointestinal tract.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 26;30(1):674. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02718-w. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40713885 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MedFusion-TransNet: multi-modal fusion via transformer for enhanced medical image segmentation.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 May 6;12:1557449. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1557449. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40395236 Free PMC article.
-
An adaptive deep learning approach based on InBNFus and CNNDen-GRU networks for breast cancer and maternal fetal classification using ultrasound images.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):22027. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-03402-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40593964 Free PMC article.
-
GBCHV an advanced deep learning anatomy aware model for accurate classification of gallbladder cancer utilizing ultrasound images.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 28;15(1):7120. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-89232-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40016258 Free PMC article.
-
Classification of cervical cancer using Dense CapsNet with Seg-UNet and denoising autoencoders.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):31764. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82489-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Radan AP, Aleksandra Polowy J, Heverhagen A, Simillion C, Baumann M, Raio L, et al. . Cervico-vaginal placental α-macroglobulin-1 combined with cervical length for the prediction of preterm birth in women with threatened preterm labor. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2020) 99:357–63. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13744, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ye J., Liu R., Zou B., Zhang H., Han C., Yang Y., et al. ., A deep convolutional neural network based hybrid framework for fetal head standard plane identification. Authorea Preprints; (2020).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

