Effect of supplementation with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG powder on intestinal and liver damage in broiler chickens challenged by lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 39534507
- PMCID: PMC11555397
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1466274
Effect of supplementation with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG powder on intestinal and liver damage in broiler chickens challenged by lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
This study explores the effect of dietary along with Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG) powder on intestinal and liver damage in broiler chickens challenged by lipopolysaccharide (LPS). A total of 100 healthy 1-day-old Ross 308 broiler chickens were selected and randomly divided into two treatments: the control group and the LGG treatment group. There were five replicates for each group, with 10 chickens per replicate. The chickens in the control group were fed a basal diet, while LGG treatment was supplemented with 1,000 mg/kg LGG along with the basal diet. The experiment lasted 29 days, and the trial included two phases. During the first 27 days, the animals were weighed on the 14th and 27th days to calculate growth performance. Then, on day 29, 2 animals from each replicate were intraperitoneally injected with 1 mg/kg BW LPS, and another 2 animals were treated with an equal volume of saline. The chickens were slaughtered 3 h later for sampling and further analysis. (1) LGG addition to the diet did not affect growth performance, including average daily gain (ADG), average daily feed intake (ADFI), and feed-to-weight ratio (F/G) of broiler chickens; (2) LPS stimulation decreased villus height (VH), and caused oxidative stress and increased the amount of diamine oxidase (DAO) in plasma, and the relative expression of intestinal inflammation genes (interleukin-8 [IL-8], interleukin 1β [IL-1β], inducible nitric oxide synthase [iNOS], and tumor necrosis factor-α [TNF-α]) and the relative expression of liver injury genes (b-cell lymphoma 2 [BCL2], heat shock protein70 [HSP70], and matrix metallopeptidase 13 [MMP13]). (3) Supplementation of LGG increased VH and the relative expression of intestinal barrier genes (mucins 2 [Mucin2] and occludin [Occludin]) and decreased the amount of DAO in plasma and the relative expression of intestinal inflammatory factors (IL-8, iNOS, and IL-1β). LGG supplementation also increased the expression of liver injury-related genes (MMP13 and MMP9). In conclusion, LGG enhanced intestinal barrier function, improved intestinal morphology, and alleviated the intestines' inflammatory response in LPS-stimulated broiler chicken, and it has a slightly protective effect on liver damage.
Keywords: Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; broiler chicken; intestinal health; lipopolysaccharide; liver.
Copyright © 2024 Zhang, Sun, Wu, Yu, Zhao, Wang, Zhang, Yi, Hou and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
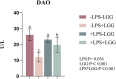
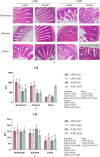
 ” marked the site of villous damage. (b) Villus height (VH). (c) Crypt depth (CD). a, b, and c: Different alphabets denote differences in significant difference (p < 0.05). LGG, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; LPS, lipopolysaccharide.
” marked the site of villous damage. (b) Villus height (VH). (c) Crypt depth (CD). a, b, and c: Different alphabets denote differences in significant difference (p < 0.05). LGG, Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG; LPS, lipopolysaccharide.Similar articles
-
Dietary l-threonine supplementation attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses and intestinal barrier damage of broiler chickens at an early age.Br J Nutr. 2018 Jun;119(11):1254-1262. doi: 10.1017/S0007114518000740. Br J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 29770758 Clinical Trial.
-
Dietary pterostilbene supplementation attenuates intestinal damage and immunological stress of broiler chickens challenged with lipopolysaccharide.J Anim Sci. 2020 Jan 1;98(1):skz373. doi: 10.1093/jas/skz373. J Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 31822918 Free PMC article.
-
Dietary taurine supplementation attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses and oxidative stress of broiler chickens at an early age.J Anim Sci. 2020 Oct 1;98(10):skaa311. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa311. J Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32954422 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of dietary pyrroloquinoline quinone disodium supplementation on inflammatory responses, oxidative stress, and intestinal morphology in broiler chickens challenged with lipopolysaccharide.Poult Sci. 2020 Nov;99(11):5389-5398. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.08.007. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 33142455 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of lipopolysaccharides from pathogenic bacteria on broiler chickens' productivity: a meta-analysis.Br Poult Sci. 2024 Dec;65(6):708-721. doi: 10.1080/00071668.2024.2364331. Epub 2024 Jun 28. Br Poult Sci. 2024. PMID: 38940295 Review.
Cited by
-
Dietary supplementation with farnesol confers a protective effect on the intestine of broiler chickens challenged with lipopolysaccharide by reshaping intestinal flora structure and regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Poult Sci. 2025 Apr;104(4):104942. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2025.104942. Epub 2025 Feb 23. Poult Sci. 2025. PMID: 40010048 Free PMC article.
-
Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides Alleviate LPS-Induced Liver Injury in Chicks by Suppressing Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Through the PPAR Signaling Pathway.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Mar 31;14(4):418. doi: 10.3390/antiox14040418. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40298760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al-Sadi R., Youssef M., Rawat M., Guo S., Dokladny K., Haque M., et al. . (2019). MMP-9-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight permeability is mediated by p38 kinase signaling pathway activation of MLCK gene. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 316, G278–G290. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00126.2018, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aravind K. L., Patil V. S., Devegowda G., Umakantha B., Ganpule S. P. (2003). Efficacy of esterified glucomannan to counteract mycotoxicosis in naturally contaminated feed on performance and serum biochemical and hematological parameters in broilers. Poult. Sci. 82, 571–576. doi: 10.1093/ps/82.4.571, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

