CardiLect: A combined cross-species lectin histochemistry protocol for the automated analysis of cardiac remodelling
- PMID: 39535377
- PMCID: PMC11911624
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.15155
CardiLect: A combined cross-species lectin histochemistry protocol for the automated analysis of cardiac remodelling
Abstract
Background: Cardiac remodelling, a crucial aspect of heart failure, is commonly investigated in preclinical models by quantifying cardiomyocyte cross-sectional area (CSA) and microvascular density (MVD) via histological methods, such as immunohistochemistry. To achieve this, optimized protocols are needed, and the species specificity is dependent on the antibody used. Lectin histochemistry offers several advantages compared to antibody-based immunohistochemistry, including as cost-effectiveness and cross-species applicability. Direct comparisons between the two methods are lacking from the literature.
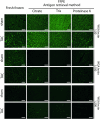
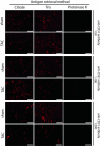
Methods and results: In this study, we compared antibody- and lectin-based methods for the histological assessment of cardiomyocyte CSA (with the use of anti-laminin and wheat germ agglutinin [WGA]) and microvascular density (utilizing anti-CD31 and isolectin B4 [ILB4]) using different embedding and antigen/carbohydrate retrieval techniques. Here, we describe a detailed, easy-to-use combined lectin histochemistry protocol (WGA and ILB4, 'CardiLect' protocol) for the histological assessment of cardiac remodelling. The lectin-based approach has been evaluated on a cross-species basis, and its efficacy has been demonstrated in zebrafish, rodents, large animals and human samples. We provide an ImageJ script ('CardiLect Analyser') for automated image analysis, validated in a preclinical heart failure model by correlating histological parameters with echocardiographic findings. CSA showed a significant positive correlation with left ventricular (LV) mass (P = 0.0098, rS = 0.7545) and significant negative correlation with markers of systolic function, such as ejection fraction (EF) (P = 0.0402, rS = -0.6364). Microvascular density showed significant negative correlation with LV mass (P = 0.0055, rS = -0.7622) and significant positive correlation with EF (P = 0.0106, rS = 0.7203).
Conclusions: The described combined lectin histochemistry protocol with the provided ImageJ script is an easy-to-use, cost-effective, cross-species approach for the histological assessment of cardiac remodelling.
Keywords: Cardiac remodelling; Echocardiography; Heart failure; Immunohistochemistry; Lectin; Transverse aortic constriction.
© 2024 The Author(s). ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
P.F. is the founder and CEO of Pharmahungary Group, a group of R&D companies. All other authors have no conflicts of interest to report.
Figures






Similar articles
-
[Expression of connective tissue growth factor in cardiomyocyte of young rats with heart failure and benazepril intervention].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006 Oct;44(10):733-7. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2006. PMID: 17229371 Chinese.
-
Matairesinol blunts adverse cardiac remodeling and heart failure induced by pressure overload by regulating Prdx1 and PI3K/AKT/FOXO1 signaling.Phytomedicine. 2024 Dec;135:156054. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.156054. Epub 2024 Sep 15. Phytomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39306883
-
Novel mouse model of left ventricular pressure overload and infarction causing predictable ventricular remodelling and progression to heart failure.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015 Jan;42(1):33-40. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12318. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25311547 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulation of soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) by riociguat attenuates heart failure and pathological cardiac remodelling.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Jun;179(11):2430-2442. doi: 10.1111/bph.15333. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33247945 Review.
-
Clinical aspects of left ventricular diastolic function assessed by Doppler echocardiography following acute myocardial infarction.Dan Med Bull. 2001 Nov;48(4):199-210. Dan Med Bull. 2001. PMID: 11767125 Review.
Cited by
-
Tirzepatide, a dual GIP/GLP1-receptor co-agonist preserves cardiac function and improves survival in angiotensin II-induced heart failure model in mice: comparison to liraglutide.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Jun 14;24(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02806-5. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40517248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Porter GA, Palade GE, Milici AJ. Differential binding of the lectins Griffonia simplicifolia I and Lycopersicon esculentum to microvascular endothelium: organ‐specific localization and partial glycoprotein characterization. Eur J Cell Biol 1990;51:85‐95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

