Loop33 × 123 CAR-T targeting CD33 and CD123 against immune escape in acute myeloid leukemia
- PMID: 39535595
- PMCID: PMC11561222
- DOI: 10.1007/s00262-024-03847-7
Loop33 × 123 CAR-T targeting CD33 and CD123 against immune escape in acute myeloid leukemia
Abstract
Background: Immunotherapy, such as chimeric antigen receptor T (CAR-T) cells targeting CD33 or CD123, has been well developed over the past decade for the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia (AML). However, the inability to sustain tumor-free survival and the possibility of relapse due to antigen loss have raised concerns. A dual targeting of CD33 and CD123 is needed for better outcomes.
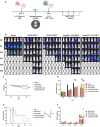
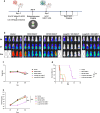
Methods: Based on our previously constructed CD33 and CD123 monovalent CAR-T, Loop33 × 123 and Loop123 × 33 CAR-T were constructed with molecular cloning techniques. All CAR-T cells were generated by lentivirus transduction of T cells from healthy donors. Phenotype detection was evaluated on day 7 concerning activation, exhaustion, and subtype proportions. Coculture killing assays were conducted using various AML cell lines and primary AML cells. Degranulation and cytokine secretion levels were detected by flow cytometry. Cell-derived xenograft models were established using wild-type Molm 13 cell lines, or a mixture of Molm 13-KO33 and Molm 13-KO123 cells as an ideal model of immune escape. By monitoring body weight and survival of tumor-bearing mice, Loop33 × 123 and Loop123 × 33 CAR-T cells were further assessed for their efficacy in vivo.
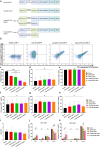
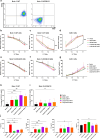
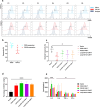
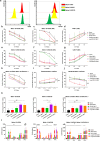
Results: In vitro study, our results demonstrated that Loop33 × 123 CAR-T cells could efficiently eliminate AML cell lines and primary AML cells with elevated degranulation and cytokine secretion levels. Compared with our previously constructed monovalent CD33 or CD123 CAR-T cells, Loop33 × 123 CAR-T cells showed superior advantages in an immune escape model. In vivo studies further confirmed that Loop33 × 123 CAR-T cells could effectively prolong the survival of mice without significant toxicity. However, Loop123 × 33 CAR-T cells failed to show the same effects. Furthermore, Loop33 × 123 CAR-T cells efficiently circumvented potential immune escape, a challenge where monovalent CAR-T cells failed.
Conclusions: Loop33 × 123 CAR-T targeting CD33 and CD123 could efficiently eliminate AML cells and prolong survival of tumor-bearing mice, while addressing the issue of immune escape.
Keywords: AML; CD123; CD33; Chimeric antigen receptor.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A (2023) Cancer statistics, 2023. CA A Cancer J Clinic 73(1):17–48. 10.3322/caac.21763 - PubMed
-
- Short NJ, Konopleva M, Kadia TM, Borthakur G, Ravandi F, DiNardo CD et al (2020) Advances in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia: new drugs and new challenges. Cancer Discov 10(4):506–525 - PubMed
-
- June CH, O’Connor RS, Kawalekar OU, Ghassemi S, Milone MC (2018) CAR T cell immunotherapy for human cancer. Science (New York, NY) 359(6382):1361–1365 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021YFC2500300/National Key Research & Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2500300/National Key Research & Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2500300/National Key Research & Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2500300/National Key Research & Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2500300/National Key Research & Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2500300/National Key Research & Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2500300/National Key Research & Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2500300/National Key Research & Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2500300/National Key Research & Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2500300/National Key Research & Development Program of China
- 2021YFC2500300/National Key Research & Development Program of China
- 82341213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82341213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82341213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82341213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82341213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82341213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82341213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82341213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82341213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82341213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 82341213/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2021-I2M-1-041/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-041/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-041/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-041/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-041/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-041/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-041/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-041/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-041/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-041/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
- 2021-I2M-1-041/CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

