Monitoring soil salinization and waterlogging in the northeastern Nile Delta linked to shallow saline groundwater and irrigation water quality
- PMID: 39537729
- PMCID: PMC11561257
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-77954-x
Monitoring soil salinization and waterlogging in the northeastern Nile Delta linked to shallow saline groundwater and irrigation water quality
Abstract
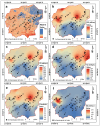
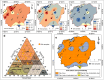
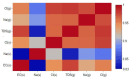
Soil salinization and waterlogging are critical environmental issues affecting agricultural productivity and cultural heritage preservation, particularly in arid regions. This study investigated soil degradation processes in the archaeologically and agriculturally significant northeastern Nile Delta of Egypt. The objective was to assess the severity of soil degradation and identify key drivers related to water resources and soil characteristics to aid in the development of management strategies. The research employed a multi-faceted approach, including hydrochemical analyses (of groundwater, irrigation water, and soil), water quality indices calculations, statistical analyses, and satellite data. The results revealed high levels of soil salinization in the northern and central areas, with 64% of soil samples classified as strongly and very strongly saline. Soil chemistry indicated salinization sources linked to sodium chloride dominance. Satellite data from Sentinel-2 images and SRTM digital elevation data showed widespread severe waterlogging in the northern lowlands. The Irrigation Water Quality Index (IWQI) values indicated that 87.5% of irrigation water samples posed severe restrictions due to high salinity and sodium hazards, which were mismatched with the low soil permeability observed in 81% of the collected samples exhibiting clay texture and covering most of the study area. Furthermore, shallow groundwater at depths of 0.5-3 m with high salinity was detected, where total dissolved solids exceeded 20,000 mg/L, and Na-Cl water types prevailed, indicating saltwater intrusion. A strong positive correlation (r > 0.83) was found between shallow saline groundwater and soil salinity. The combination of poor irrigation water quality, shallow saline groundwater tables, and low-permeability soils created a synergistic effect that severely compromised soil health and agricultural productivity. It also posed severe risks to the structural integrity of archaeological sites and buried artifacts through accelerated physical and chemical weathering processes. This necessitates an urgent mitigation strategy to combat soil degradation in this critical area.
Keywords: Archaeological site deterioration; Correlation analysis; Irrigation water quality; Kriging interpolation; Soil degradation; Spectral water indices; Water quality indices.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Assessment of hydrochemical characteristics, health risks and quality of groundwater for drinking and irrigation purposes in a mountainous region of Pakistan.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024 Jul;31(31):43967-43986. doi: 10.1007/s11356-024-34046-7. Epub 2024 Jun 25. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38918296 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of soil salinity and water-salt transport in the vadose zone of salt-impacted regions with variable permeability.Environ Geochem Health. 2024 Sep 24;46(11):442. doi: 10.1007/s10653-024-02223-9. Environ Geochem Health. 2024. PMID: 39316201 Free PMC article.
-
Saltwater intrusion and land subsidence destroy northern Nile Delta archaeological sites: An assessment using hydrochemical indices, SAR satellite imagery, and analytic hierarchy process (AHP).Mar Pollut Bull. 2025 Mar;212:117460. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2024.117460. Epub 2024 Dec 26. Mar Pollut Bull. 2025. PMID: 39729832
-
Salinization of groundwater during 20 years of agricultural irrigation, Luxor, Egypt.Environ Geochem Health. 2022 Nov;44(11):3821-3835. doi: 10.1007/s10653-021-01135-2. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Environ Geochem Health. 2022. PMID: 34698983
-
A review of the distribution, sources, genesis, and environmental concerns of salinity in groundwater.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Nov;27(33):41157-41174. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-10354-6. Epub 2020 Aug 19. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32815007 Review.
References
-
- Zaghloul, E. A., Abdeen, M. M., Elbeih, S. F. & Soliman, M. A. Water logging problems in Egypt’s deserts: Case study Abu Mena archaeological site using geospatial techniques. Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Space Sci.23(3), 387–399 (2020).
-
- Singh, A. Soil salinization management for sustainable development: A review. J. Environ. Manage.277, 111383 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Han, W., Gong, R., Liu, Y. & Gao, Y. Influence mechanism of salt erosion on the earthen heritage site wall in Pianguan Bastion. Case Stud. Constr. Mater.17, e01388 (2022).
-
- Polykretis, C. et al. Assessment of water-induced soil erosion as a threat to cultural heritage sites: The case of Chania prefecture, Crete Island, Greece. Big Earth Data. 6(4), 561–579 (2022).
-
- Zhang, Y. Knowledge of earthen heritage deterioration in dry areas of China: Salinity effect on the formation of cracked surface crust. Herit. Sci.11(1), 41 (2023).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

