The abscopal effects of sonodynamic therapy in cancer
- PMID: 39537767
- PMCID: PMC11876350
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-024-02898-y
The abscopal effects of sonodynamic therapy in cancer
Abstract
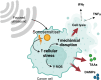
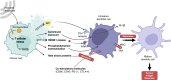
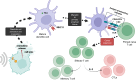
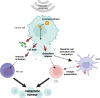
The abscopal effect is a phenomenon wherein localised therapy on the primary tumour leads to regression of distal metastatic growths. Interestingly, various pre-clinical studies utilising sonodynamic therapy (SDT) have reported significant abscopal effects, however, the mechanism remains largely enigmatic. SDT is an emerging non-invasive cancer treatment that uses focussed ultrasound (FUS) and a sonosensitiser to induce tumour cell death. To expand our understanding of abscopal effects of SDT, we have summarised the preclinical studies that have found SDT-induced abscopal responses across various cancer models, using diverse combination strategies with nanomaterials, microbubbles, chemotherapy, and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Additionally, we shed light on the molecular and immunological mechanisms underpinning SDT-induced primary and metastatic tumour cell death, as well as the role and efficacy of different sonosensitisers. Notably, the observed abscopal effects underscore the need for continued investigation into the SDT-induced 'vaccine-effect' as a potential strategy for enhancing systemic anti-tumour immunity and combating metastatic disease. The results of the first SDT human clinical trials are much awaited and are hoped to enable the further evaluation of the safety and efficacy of SDT, paving the way for future studies specifically designed to explore the potential of translating SDT-induced abscopal effects into clinical reality.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sonodynamic therapy-assisted immunotherapy: A novel modality for cancer treatment.Cancer Sci. 2018 May;109(5):1330-1345. doi: 10.1111/cas.13578. Epub 2018 May 7. Cancer Sci. 2018. PMID: 29575297 Free PMC article.
-
Nanosonosensitizer-Augmented Sonodynamic Therapy Combined with Checkpoint Blockade for Cancer Immunotherapy.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Mar 5;16:1889-1899. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S290796. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 33707944 Free PMC article.
-
Exploiting a Rose Bengal-bearing, oxygen-producing nanoparticle for SDT and associated immune-mediated therapeutic effects in the treatment of pancreatic cancer.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021 Jun;163:49-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2021.03.005. Epub 2021 Mar 31. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2021. PMID: 33798727
-
Design and Challenges of Sonodynamic Therapy System for Cancer Theranostics: From Equipment to Sensitizers.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Mar 12;8(10):2002178. doi: 10.1002/advs.202002178. eCollection 2021 May. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34026428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sonodynamic therapy-derived multimodal synergistic cancer therapy.Cancer Lett. 2021 Jan 28;497:229-242. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.037. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Cancer Lett. 2021. PMID: 33122099 Review.
References
-
- Lafond M, Yoshizawa S, Umemura S. Sonodynamic therapy: advances and challenges in clinical translation. J Ultrasound Med. 2019;38:567–80. - PubMed
-
- Rosenthal I, Sostaric JZ, Riesz P. Sonodynamic therapy—a review of the synergistic effects of drugs and ultrasound. Ultrason Sonochem. 2004;11:349–63. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

