MRI Radiomics-Based Machine Learning to Predict Lymphovascular Invasion of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 39538052
- PMCID: PMC12343420
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-024-01329-x
MRI Radiomics-Based Machine Learning to Predict Lymphovascular Invasion of HER2-Positive Breast Cancer
Abstract
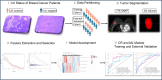
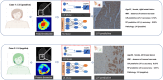
This study aims to develop and prospectively validate radiomic models based on MRI to predict lymphovascular invasion (LVI) status in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer. A total of 225 patients with HER2-positive breast cancer who preoperatively underwent breast MRI were selected, forming the training set (n = 99 LVI-positive, n = 126 LVI-negative). A prospective validation cohort included 130 patients with breast cancer from the Affiliated Zhongshan Hospital of Dalian University (n = 57 LVI-positive, n = 73 LVI-negative). A total of 390 radiomic features and eight conventional radiological characteristics were extracted. For the optimum feature selection phase, the LASSO regression model with tenfold cross-validation (CV) was employed to identify features with non-zero coefficients. The conventional radiological (CR) model was determined based on visual morphological (VM) features and the optimal radiomic features correlated with LVI, identified through multivariate logistic analyses. Subsequently, various machine learning (ML) models were developed using algorithms such as support vector machine (SVM), k-nearest neighbor (KNN), gradient boosting machine (GBM), and random forest (RF). The performance of ML and CR models. The results show that the AUC of the CR model in the training and validation sets were 0.81 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.74-0.86) and 0.82 (95% CI, 0.69-0.89), respectively. The ML model achieved the best performance, with AUCs of 0.96 (95% CI, 0.99-1.00) in the training set and 0.95 (95% CI, 0.89-0.96) in the validation set. There were significant differences between the CR and ML models in predicting LVI status. Our study demonstrated that the machine learning models exhibited superior performance in predicting LVI status based on pretreatment MRI compared to the CR model, which does not necessarily rely on a priori knowledge of visual morphology.
Keywords: Breast cancer; HER2-positive; MRI; Machine learning; Radiomic.
© 2024. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics Approval: This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of the First Hospital of Qinhuangdao (2024K006). Consent to Participate: Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Competing Interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A: Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin 2020, 70(1):7-30. - PubMed
-
- Zhao Y, Yang N, Wang X, Huang Y, Zhou X, Zhang D: Potential roles of lymphovascular space invasion based on tumor characteristics provide important prognostic information in T1 tumors with ER and HER2 positive breast cancer. Clinical & translational oncology : official publication of the Federation of Spanish Oncology Societies and of the National Cancer Institute of Mexico 2020, 22(12):2275-2285. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
