Prognostic role of Androgen Receptor splice variant 7 (AR-V7) in the pathogenesis of breast cancer
- PMID: 39538154
- PMCID: PMC11562864
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-024-13165-x
Prognostic role of Androgen Receptor splice variant 7 (AR-V7) in the pathogenesis of breast cancer
Abstract
Background: The Androgen Receptor (AR) has emerged as an endocrine therapy target in Breast Cancer, exhibiting up to 80% expression in clinical cases. AR-V7, a constitutively activated splice variant of AR with a truncated ligand-binding domain (LBD), demonstrates ligand-independent transcriptional activity and resistance to nonsteroidal antiandrogens like Bicalutamide or Enzalutamide, targeting the LBD. In metastatic prostate cancer, elevated AR-V7 levels lead to therapeutic resistance and increased metastasis.
Methods: In this study, we evaluated the expression of AR and AR-V7 in cell lines and a cohort of 89 patients undergoing surgical intervention for treatment-naïve breast cancer. Further clinicopathological correlations and survival analysis were performed to evaluate the relationship between the AR and AR-V7 expression and clinical outcomes.
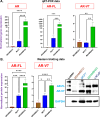
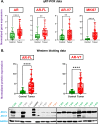
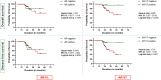
Results: AR-V7/AR-FL ratio was elevated in the TNBC cell line and downregulation of AR-FL upon AR antagonists' treatment led to a compensatory increase in AR-V7. Clinical samples showed significantly elevated expression of AR and AR-V7 in tumors compared to control cases. Further clinicopathological correlation revealed aggressive clinical traits, higher pathological grades, and poor survival with AR-V7 expression.
Conclusions: Our study unravels AR-V7 as a marker for poor clinical outcomes, predicting breast cancer aggressiveness, and encourages consideration of AR-V7 as a probable target for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: AR-V7; Androgen receptor; Biomarker; Breast cancer; Splice variant.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I et al. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians [Internet] [cited 2024 May 2];n/a(n/a). https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.3322/caac.21834 - PubMed
-
- Huang WY, Newman B, Millikan RC, Schell MJ, Hulka BS, Moorman PG. Hormone-related factors and risk of breast Cancer in relation to Estrogen Receptor and progesterone receptor status. Am J Epidemiol. 2000;151(7):703–14. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

