Higher interest to continue COVID-19 practice recommendations in non-pandemic times among German GPs with better crisis leadership skills (egePan study)
- PMID: 39538285
- PMCID: PMC11562362
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-024-11855-7
Higher interest to continue COVID-19 practice recommendations in non-pandemic times among German GPs with better crisis leadership skills (egePan study)
Abstract
Background: The German College of General Practitioners and Family Physicians (DEGAM) issued a COVID-19 guideline with eleven recommendations to support primary care services during the pandemic. Their use in general practices beyond the pandemic can contribute to pandemic preparedness. This study analysed general practitioners' (GPs) interest in applying recommended organisational changes in non-pandemic times.
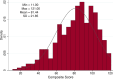
Methods: Data from the German egePan GP survey (n = 516 GPs) - a multi-level clustered randomised web-based survey - were analysed. GPs' interest in the future application of the eleven guideline recommendations was calculated. In addition, each recommendation was evaluated by the GPs using a Net-Promoter-Score (NPS range - 100 to 100). A linear regression model identified GP and practice characteristics associated with a higher interest in applying recommendations in non-pandemic times.
Results: 98.5% of the GPs indicated the intention to implement at least one guideline recommendation prospectively: disinfectant dispensers at the entrance (86%), optimised consultation scheduling to reduce waiting times (83%), and glass screens in the reception area (72%), which also received the highest NPS scores. In contrast, lower interest was observed for items such as insurance card readers handled by patients (48%), only selected staff treating infectious patients (44%), and video consultations for patients with infections (26%). A higher interest to implement recommendations in non-pandemic times was associated with a higher crisis leadership score (p < 0.001), using the Corona-Warn-App (p = 0.007), and being a female GP (p = 0.045). In addition, GPs from Western, Northern, and Southern, and those with a higher patient volume per three months, were more interested in future implementation.
Conclusions: Overall, GPs demonstrated the readiness to follow the DEGAM COVID-19 guideline outside pandemic periods, establishing them as key contributors to pandemic preparedness in Germany.
Keywords: COVID-19; General practice changes; General practitioners; Nationwide survey; Pandemic preparedness; Primary care.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
The aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic in general practices compared to pre-pandemic times: Longitudinal questionnaire survey among general practitioners and medical practice assistants in Germany on how the pandemic shaped everyday care.Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundhwes. 2025 Jun;195:51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.zefq.2025.02.002. Epub 2025 Mar 5. Z Evid Fortbild Qual Gesundhwes. 2025. PMID: 40050155
-
German GPs' Self-Perceived Role in the COVID-19 Pandemic: Leadership, Participation in Regional Services and Preferences for Future Pandemic Preparedness.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jun 9;20(12):6088. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20126088. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37372676 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the German living guideline "Protection against the Overuse and Underuse of Health Care" - an online survey among German GPs.BMC Prim Care. 2024 Dec 12;25(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12875-024-02657-1. BMC Prim Care. 2024. PMID: 39668346 Free PMC article.
-
How GPs adapted their practices and organisations at the beginning of COVID-19 outbreak: a French national observational survey.BMJ Open. 2020 Dec 2;10(12):e042119. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-042119. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 33268433 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating clinical guidelines for chronic disease management: Do they enable the personalization of care?Public Health. 2025 Jan;238:131-138. doi: 10.1016/j.puhe.2024.11.023. Epub 2024 Dec 8. Public Health. 2025. PMID: 39652981
References
-
- Aretz B, Krumpholtz Y, Kugai S, Amarell N, Schmidt M, Eggers D et al. egePan GP survey: a questionnaire to assess the experiences of German general practitioners during the COVID-19 pandemic. 2023. 10.17632/gsybsm6rcw.1.
-
- Blankenfeld H, Kaduszkiewicz H, Kochen MM, Pömsl J, Scherer M. SARS-CoV-2/ Covid-19-Informationen & Praxishilfen für niedergelassene Hausärztinnen und Hausärzte. DEGAM S1-Handlungsempfehlung. 19. Aufl. Hg. v. Deutsche Gesellschaft für Allgemeinmedizin und Familienmedizin e.V; 2021. Online verfügbar unter https://www.degam.de/files/Inhalte/Leitlinien-Inhalte/Dokumente/DEGAM-S1..., zuletzt geprüft am 08.10.2021.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical