The influence of family socioeconomic status on college students' mental health literacy: the chain mediating effect of parenting styles and interpersonal relationships
- PMID: 39539306
- PMCID: PMC11557463
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1477221
The influence of family socioeconomic status on college students' mental health literacy: the chain mediating effect of parenting styles and interpersonal relationships
Abstract
Introduction: With the increasing prevalence of mental health challenges among college students, understanding how family background and interpersonal dynamics affect mental health literacy is critical. This study examined the relationships between family socioeconomic status, mental health literacy, parenting styles, and interpersonal relationships among 1,107 college students.
Methods: Using an online questionnaire, the study explored how family socioeconomic status, parenting styles, and interpersonal relationships influence mental health literacy.
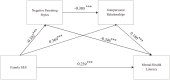
Results and discussion: The results showed that family socioeconomic status significantly and positively predicts mental health literacy. Both positive and negative parenting styles were found to partially mediate the relationship between family socioeconomic status and mental health literacy. Additionally, interpersonal relationships partially mediated this relationship. Finally, the study revealed that positive and negative parenting styles acted as sequential mediators between family socioeconomic status and mental health literacy through interpersonal relationships. These findings provide insights into the mechanisms by which family socioeconomic factors shape mental health literacy among college students.
Keywords: chain mediating role; family socioeconomic status; interpersonal relationships; mental health literacy; parenting styles.
Copyright © 2024 Wu, Shen, Shen, Liao and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The Influence of Family Socioeconomic Status on Primary School Students' Emotional Intelligence: The Mediating Effect of Parenting Styles and Regional Differences.Front Psychol. 2022 Feb 21;13:753774. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.753774. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 35264997 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the role of self-efficacy and interpersonal relationships in the relationship between subjective family socio-economic status and college students' trust character: a case study of a university in Shaanxi Province, China.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 4;15(1):11543. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-96358-z. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40185888 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of paternal-maternal parenting styles on college students' internet addiction of different genders: The mediating role of life satisfaction.PLoS One. 2024 May 14;19(5):e0303554. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303554. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38743694 Free PMC article.
-
Does more support mean more literacy? The relationship and mechanisms between digital support and college students' digital literacy.Front Psychol. 2025 Apr 16;16:1571926. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1571926. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40337717 Free PMC article.
-
Family socioeconomic status and young children digital addiction: a moderated mediation model.Front Psychol. 2024 Sep 27;15:1435575. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1435575. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39399265 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arrindell W. A., Sanavio E., Aguilar G., Sica C., Hatzichristou C., Eisemann M., et al. . (1999). The development of a short form of the EMBU: its appraisal with students in Greece, Guatemala, Hungary and Italy1. Personal. Individ. Differ. 27, 613–628. doi: 10.1016/S0191-8869(98)00192-5 - DOI
-
- Bai J. (2019). The study of redistributive preferences for different social classes. Doctoral dissertation, Central China Normal University.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

