Reliability of mpMRI in diagnosing cancer prostate following intravesical BCG for bladder cancer
- PMID: 39539555
- PMCID: PMC11557261
- DOI: 10.1002/bco2.446
Reliability of mpMRI in diagnosing cancer prostate following intravesical BCG for bladder cancer
Erratum in
-
Erratum.BJUI Compass. 2024 Dec 30;5(12):1324-1329. doi: 10.1002/bco2.482. eCollection 2024 Dec. BJUI Compass. 2024. PMID: 39744071 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Detecting carcinoma prostate (CaP) after intravesical Bacillus Calmette Guerin (BCG) immunotherapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) poses diagnostic challenges. Granulomatous prostatitis (GP) has an incidence of 0.8%-3.3% in post-intravesical BCG patients and 6% incidence in a PIRADS 5 lesion on multiparametric MRI (mpMRI). Patients with GP after intravesical BCG may have clinical, biochemical, and radiological features similar to CaP. In our study, we evaluate the reliability of mpMRI in diagnosing CaP after intravesical BCG therapy.
Materials and methods: We reviewed the NMIBC patients treated with intravesical BCG therapy between 2017 and 2023 and investigated those who underwent mpMRI and MR fusion biopsy in suspicion of CaP. A total of 120 patients had intravesical BCG immunotherapy, and 10 patients met our selection criteria. We performed a descriptive analysis of these patients and assessed the sensitivity and specificity of mpMRI in diagnosing CaP.
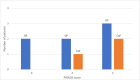
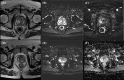
Results: The sensitivity of mpMRI in detecting CaP was 100%, and the specificity was 28.6%. Similarly, the negative predictive value for detecting CaP was 100%, and the positive predictive value was 37.5%. Among patients evaluated with mpMRI, a PIRADS 4 or 5 lesion was seen in 8 (80%) patients, and there was no lesion in 2 (20%) patients. The mpMRI detected 1 lesion in 6 patients (60%) and 2 (20%) in 2 patients. The lesions had a PIRADS score of 4 and 5 in 6 (60%) and 2 (20%) patients, respectively. Among these lesions, 8 (80%) were in the peripheral zone and 2 (20%) in the transition zone. In the MR fusion biopsy of these 10 patients, 7 (70%) had granulomatous prostatitis, and 3 (30%) had CaP.
Conclusion: In our study on evaluating the reliability of mpMRI in diagnosing CaP among post-intravesical BCG patients, we noted that although PIRADS in mpMRI had high sensitivity in identifying prostate lesions, its specificity for detecting CaP is limited.
Keywords: cancer prostate; granulomatous prostatitis; intravesical BCG; mpMRI; non‐muscle invasive bladder cancer.
© 2024 The Author(s). BJUI Compass published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of BJU International Company.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Brausi M, Oddens J, Sylvester R, Bono A, van de Beek C, van Andel G, et al. Side effects of Bacillus Calmette‐Guérin (BCG) in the treatment of intermediate‐ and high‐risk Ta, T1 papillary carcinoma of the bladder: results of the EORTC genito‐urinary cancers group randomised phase 3 study comparing one‐third dose with full dose and 1 year with 3 years of maintenance BCG. Eur Urol 2014;65(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2013.07.021 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
