Outcome of post-prostatectomy stress urinary incontinence surgery in men with preoperative idiopathic detrusor overactivity
- PMID: 39539568
- PMCID: PMC11557267
- DOI: 10.1002/bco2.442
Outcome of post-prostatectomy stress urinary incontinence surgery in men with preoperative idiopathic detrusor overactivity
Erratum in
-
Erratum.BJUI Compass. 2024 Dec 30;5(12):1324-1329. doi: 10.1002/bco2.482. eCollection 2024 Dec. BJUI Compass. 2024. PMID: 39744071 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Urodynamic evidence of storage dysfunction such as detrusor overactivity (DO) and/or poor compliance are present in up to 30-40% of patients after Radical Prostatectomy (RP). However, the current optimal management of men with DO on preoperative urodynamics prior to male stress urinary incontinence (SUI) surgery is not known.
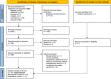
Methods: We performed a systematic search of the literature including articles on patients undergoing SUI surgery after prostatectomy with preoperative DO between January 2003 and May 2023 to ensure contemporaneous data was obtained.
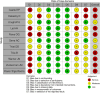
Results: We identified 11 eligible publications with a total of 792 patients. On Urodynamics, 29% (n = 229) patients had DO prior to SUI surgery. Overall 69% patients had a successful outcome after SUI surgery while 26% (132/499) failed while 34% (32/95) patients who had proven DO preoperatively failed SUI surgery. The difference was not statistically significant. Considering the sub-group analysis, the failure rate with preoperative DO was significantly higher in the sling group (43%) than in the AUS group (18%). The review was limited by the outcome heterogeneity, variability in study inclusion criteria, reporting and analysis and the quality of the available studies.
Conclusions: Within the limitations of the data, this review did not show a statistically significant higher failure rate of male incontinence surgery in patients with DO. Hence, patients with DO on preoperative urodynamics who are eligible for male SUI surgery should not be denied surgery but should be counselled appropriately of the risks and potential need for subsequent treatment, to manage expectations.
Keywords: male incontinence; overactive bladder; radical prostatectomy; storage dysfunction; stress urinary incontinence.
© 2024 The Author(s). BJUI Compass published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of BJU International Company.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Soysal P, Veronese N, Ippoliti S, Pizzol D, Carrie AM, Stefanescu S, et al. European Society of Geriatric Medicine Special Interest Group in systematic reviews, meta‐analyses. The impact of urinary incontinence on multiple health outcomes: an umbrella review of meta‐analysis of observational studies. Aging Clin Exp Res. 2023;35(3):479–495. 10.1007/s40520-022-02336-0 PMID: Epub 2023 Jan 13. PMID: 36637774. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
