Efficacy of non-invasive brain stimulation for post-stroke sleep disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39539650
- PMCID: PMC11557329
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1420363
Efficacy of non-invasive brain stimulation for post-stroke sleep disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to systematically assess the clinical efficacy of non-invasive brain stimulation (NIBS) for treating post-stroke sleep disorders (PSSD).
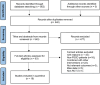
Methods: We conducted thorough literature search across multiple databases, including PubMed, Web of Science, EmBase, Cochrane Library, Scopus, China Biology Medicine (CBM); China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI); Technology Periodical Database (VIP), and Wanfang Database, focusing on RCTs examining NIBS for PSSD. Meta-analyses were performed using RevMan 5.4 and Stata 14.
Results: Eighteen articles were reviewed, including 16 on repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS), one on Theta Burst Stimulation (TBS), and two on transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS). Meta-analysis results indicated that rTMS within NIBS significantly improved the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) score (MD = -1.85, 95% CI [-2.99, -0.71], p < 0.05), the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD-17) score [MD = -2.85, 95% CI (-3.40, -2.30), p < 0.05], and serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels [MD = 4.19, 95% CI (2.70, 5.69), p < 0.05], while reducing the incidence of adverse reactions [RR = 0.36, 95% CI (0.23, 0.55), p < 0.05]. TBS significantly improved the PSQI score in patients with PSSD (p < 0.05). Conversely, tDCS significantly improved the HAMD-17 score in PSSD patients [MD = -1.52, 95% CI (-3.41, -0.64), p < 0.05]. Additionally, rTMS improved sleep parameters, including Stage 2 sleep (S2%) and combined Stage 3 and 4 sleep (S3 + S4%) (p < 0.05), while tDCS improved total sleep time (TST) and sleep efficiency (SE) (p < 0.05).Subgroup analysis results indicated: (1) Both LF-rTMS and HF-rTMS improved PSQI scores (p < 0.05). (2) Both rTMS combined with medication and rTMS alone improved PSQI scores (p < 0.05). Compared to the sham/blank group, the rTMS group showed improvements in SE, sleep latency (SL), S1%, S3 + S4%, and REM sleep (REM%). The rTMS combined with medication group showed improved SL compared to the medication-only group (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: NIBS effectively improves sleep quality, structure, depression levels, and BDNF levels in PSSD patients, while also being safe. Further investigations into the potential of NIBS in PSSD treatment may provide valuable insights for clinical applications.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, CRD42023485317.
Keywords: insomnia; meta-analysis; non-invasive brain stimulation; sleep disorder; stroke; transcranial direct current stimulation; transcranial magnetic stimulation.
Copyright © 2024 Huang, Zhang, Zhang, Li, Zhou, Yang and An.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




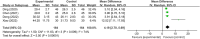


References
-
- Šiarnik P, Klobučníková K, Šurda P, Putala M, Šutovský S, Kollár B, et al. . Excessive daytime sleepiness in acute ischemic stroke: association with restless legs syndrome, diabetes mellitus, obesity, and sleep-disordered breathing. J Clin Sleep Med. (2018) 14:95–100. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.6890, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yu F, Zhang C. Expert consensus on assessment and Management of Stroke-Related Sleep Disorders in China 2023. Chin J Stroke. (2023) 18:221–39.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

