Engineered Porous Beta-Cyclodextrin-Loaded Raloxifene Framework with Potential Anticancer Activity: Physicochemical Characterization, Drug Release, and Cytotoxicity Studies
- PMID: 39539969
- PMCID: PMC11559214
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S469570
Engineered Porous Beta-Cyclodextrin-Loaded Raloxifene Framework with Potential Anticancer Activity: Physicochemical Characterization, Drug Release, and Cytotoxicity Studies
Abstract
Background: Cancer ranks as the second most common cause of mortality as depicted by the World Health Organization, with one in six deaths being cancer-related mortality. Taking the lead in females, breast cancer is the most common neoplasm. Raloxifene, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, has been utilized as a chemotherapeutic agent for the treatment of breast cancer in postmenopausal women. However, its poor aqueous solubility hinders its clinical applications. Beta-cyclodextrin-based framework is a novel class of nano-vectors that used to potentiate the solubility and dissolution rate of poorly soluble drugs.
Aim: The present study investigates the solubility and dissolution rate enhancement as well as the potential cytotoxic activity of raloxifene-loaded nanosponges formulation.
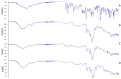
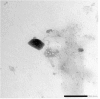
Methods: The fabrication and optimization of cyclodextrin nanosponges crosslinked with diphenyl carbonate was portrayed through stoichiometric selection of cyclodextrin-to-crosslinker ratio. The complexation phenomenon and nanosponges formation were validated using FTIR, PXRD, TEM, and SEM examination.
Results: Raloxifene-loaded nanosponges exhibited a 440±8.5 nm particle size, a negative zeta potential of 25.18±2.3 mV and a partial drug incorporation. Moreover, the drug loaded nanosponges demonstrated an in-vitro significantly enhanced dissolution behavior. Furthermore, the in-vitro cytotoxicity of the raloxifene-loaded nanosponges on MCF-7 breast cancer cell lines was statistically significant compared to the complex-free raloxifene.
Conclusion: The cytotoxic behavior provided evidence that the incorporation of raloxifene within the nanosponges structure enhanced its anticancer activity and represents a potential nanocarrier for anticancer agent delivery.
Keywords: anticancer; beta-cyclodextrin; breast cancer; nanosponges; raloxifene.
© 2024 Alwattar and Mehanna.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest are disclosed by the authors of this work.
Figures





References
-
- Richie RC, Swanson JO. Breast cancer: a review of the literature. J Insur Med. 2003;35(2):85–101. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

