The impact of exercise self-efficacy on college students' emotion management ability: an analysis of the mediating effects based on exercise behavior and screen media use
- PMID: 39540085
- PMCID: PMC11557494
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1456753
The impact of exercise self-efficacy on college students' emotion management ability: an analysis of the mediating effects based on exercise behavior and screen media use
Abstract
Objective: To explore the impact of exercise self-efficacy on college students' emotion management ability and to analyze the mediating effects of exercise behavior and screen media use between exercise self-efficacy and emotion management ability.
Methods: This study adopted stratified, whole-cluster, and staged sampling methods, using an online questionnaire that included demographic information, exercise self-efficacy, exercise behavior, screen media use, and other relevant aspects, obtaining a total of 12,687 valid questionnaires.
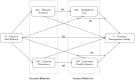
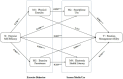
Results: The study indicated a significant positive correlation between exercise self-efficacy and emotion management ability (r = 0.349, p < 0.01). There was also a positive correlation between physical exercise and emotion management ability (r = 0.128, p < 0.01). In contrast, smartphone use showed a significant negative correlation with emotion management ability (r = -0.102, p < 0.01). Additionally, exercise persistence and electronic health literacy presented significant positive correlations with emotion management ability (r = 0.370, p < 0.01; r = 0.502, p < 0.01). Chain-mediated effect analysis revealed that exercise self-efficacy positively affected emotion management ability by enhancing physical exercise and reducing smartphone use (95% CI: [0.001, 0.002]). Furthermore, exercise self-efficacy positively influenced emotion management ability by enhancing exercise persistence and e-health literacy (95% CI: [0.029, 0.042]). These two variables acted as chain mediators, demonstrating the pathways through which exercise self-efficacy affects emotion management ability.
Conclusion: This study deepened the understanding of the interplay between exercise behavior, screen media use, and emotion management ability. It suggested that emotion management ability could be enhanced through strategies of improving exercise persistence, physical exercise, electronic health literacy, and reducing smartphone use while considering differences in gender, academic year, and regional factors in intervention programs.
Keywords: emotion management ability; exercise persistence; exercise self-efficacy; mediating effects; physical exercise; screen media use.
Copyright © 2024 Zhu, Li, Lou, Mu and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mayer JD, Salovey P. (1997). What is emotional intelligence.
-
- Kahwagi R-M, Sfeir E, Barbar S, Haddad C, Akel M, Hallit S, et al. . Investigating the relationship between the use of problematic social networks and emotional intelligence in a sample of Lebanese adults. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. (2022) 24:21m03139. doi: 10.4088/PCC.21m03139, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Caikang W. A study on the relationship between emotional intelligence and anxiety, depression, and mood of college students. Chin J Clin Psychol. (2002) 4:298–9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3611.2002.04.021 - DOI
-
- Nan Y. Research on the current situation and cultivation strategies of adolescent emotional management ability. Beijing Youth Res. (2023) 32:108–112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-4002.2023.03.014 - DOI
-
- Xiaolan Fu, Kan Zhang. (2022). Report on the development of National Mental Health in China (2021–2022). Available at: https://pdc.capub.cn/search.html#/detail?id=ohthxkrpcakmwv55jmsmpemkdhxu...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical