Loncastuximab in high-risk and heavily pretreated relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a realworld analysis from 21 US centers
- PMID: 39540227
- PMCID: PMC11873705
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2024.285977
Loncastuximab in high-risk and heavily pretreated relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: a realworld analysis from 21 US centers
Abstract
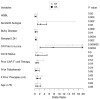
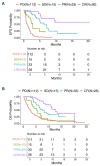
Outcomes in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) are poor. Loncastuximab- teserine (Lonca) is an antibody-drug conjugate which was approved by the Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of patients with R/R DLBCL who have received at least two prior lines of therapy, based on the results of the LOTIS-2 trial. However, there are limited data regarding its efficacy in the real-world setting. This retrospective study included 21 US centers and evaluated outcomes of patients with R/R DLBCL treated with Lonca. Our analysis comprises 187 patients with notably higher-risk baseline features compared to those of the LOTIS-2 population, including a higher proportion of patients with bulky disease (17% vs. 0%), high-grade B-cell histology (22% vs. 8%), and increased number of prior lines of therapy (median 4 vs. 3). The complete response rate was 14% and overall response rate was 32%. The median event-free survival and overall survival were 2.1 and 4.6 months, respectively. Those with bulky disease and high-grade B-cell histology had significantly worse outcomes, and those with non-germinal center cell of origin and a complete response to the most recent line of therapy demonstrated superior outcomes. In summary, in this largest retrospective cohort study of Lonca in the real-world setting, the response rates, event-free survival and overall survival were lower than those reported in LOTIS-2, which is likely reflective of its use in higher risk and more heavily pre-treated patients in the real world compared to the patients enrolled on a clinical study.
Figures

References
-
- Hagberg H, Gisselbrecht C. CORAL study group. Randomised phase III study of R-ICE versus R-DHAP in relapsed patients with CD20 diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) followed by high-dose therapy and a second randomisation to maintenance treatment with rituximab or not: an update of the CORAL study. Ann Oncol. 2006;17(Suppl 4):iv31-32. - PubMed
-
- Caimi PF, Ai W, Alderuccio JP, et al. . Loncastuximab tesirine in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (LOTIS-2): a multicentre, open-label, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22(6):790-800. - PubMed
-
- Salles G, Duell J, Barca EG, et al. . Tafasitamab plus lenalidomide in relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (L-MIND): a multicentre, prospective, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2020;21(7):978-988. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

