RiboSeq.Org: an integrated suite of resources for ribosome profiling data analysis and visualization
- PMID: 39540432
- PMCID: PMC11701704
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1020
RiboSeq.Org: an integrated suite of resources for ribosome profiling data analysis and visualization
Abstract
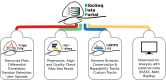
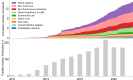
Ribosome profiling (Ribo-Seq) has revolutionised our understanding of translation, but the increasing complexity and volume of Ribo-Seq data present challenges for its reuse. Here, we formally introduce RiboSeq.Org, an integrated suite of resources designed to facilitate Ribo-Seq data analysis and visualisation within a web browser. RiboSeq.Org comprises several interconnected tools: GWIPS-viz for genome-wide visualisation, Trips-Viz for transcriptome-centric analysis, RiboGalaxy for data processing and the newly developed RiboSeq data portal (RDP) for centralised dataset identification and access. The RDP currently hosts preprocessed datasets corresponding to 14840 sequence libraries (samples) from 969 studies across 96 species, in various file formats along with standardised metadata. RiboSeq.Org addresses key challenges in Ribo-Seq data reuse through standardised sample preprocessing, semi-automated metadata curation and programmatic information access via a REST API and command-line utilities. RiboSeq.Org enhances the accessibility and utility of public Ribo-Seq data, enabling researchers to gain new insights into translational regulation and protein synthesis across diverse organisms and conditions. By providing these integrated, user-friendly resources, RiboSeq.Org aims to lower the barrier to reproducible research in the field of translatomics and promote more efficient utilisation of the wealth of available Ribo-Seq data.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
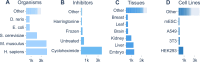
Similar articles
-
RiboGalaxy: A Galaxy-based Web Platform for Ribosome Profiling Data Processing - 2023 Update.J Mol Biol. 2023 Jul 15;435(14):168043. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168043. Epub 2023 Mar 9. J Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37356899
-
RiboGalaxy: A browser based platform for the alignment, analysis and visualization of ribosome profiling data.RNA Biol. 2016;13(3):316-9. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2016.1141862. Epub 2016 Jan 29. RNA Biol. 2016. PMID: 26821742 Free PMC article.
-
GWIPS-viz: development of a ribo-seq genome browser.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(Database issue):D859-64. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1035. Epub 2013 Oct 31. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24185699 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in ribosome profiling technologies.Biochem Soc Trans. 2025 Jun 30;53(3):555-564. doi: 10.1042/BST20253061. Biochem Soc Trans. 2025. PMID: 40380882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the potential of large language model-based chatbots in challenges of ribosome profiling data analysis: a review.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Nov 22;26(1):bbae641. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae641. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 39668339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Complete Loss of PAX4 causes Transient Neonatal Diabetes in Humans.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Apr 3:2025.04.01.25324926. doi: 10.1101/2025.04.01.25324926. medRxiv. 2025. Update in: Mol Metab. 2025 Sep;99:102201. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2025.102201. PMID: 40236391 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Baudin-Baillieu A., Hatin I., Legendre R., Namy O.. Translation analysis at the genome scale by ribosome profiling. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016; 1361:105–24. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

