Hyponatremia Associated with the Use of Common Antidepressants in the All of Us Research Program
- PMID: 39540435
- PMCID: PMC11739749
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.3484
Hyponatremia Associated with the Use of Common Antidepressants in the All of Us Research Program
Abstract
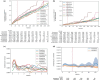
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI), serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI), and norepinephrine-dopamine reuptake inhibitor (NRI) antidepressants can cause hyponatremia through syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). This study assesses the differential risks of hyponatremia associated with commonly prescribed SSRIs (fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline, citalopram, escitalopram), SNRIs (duloxetine, venlafaxine) and NRI (bupropion), as well as omeprazole as a reference, with a retrospective observational cohort study in the All of Us Research Program, a national multicenter research cohort containing de-identified electronic health records (EHR). Participants who had been prescribed monotherapy with any of eight common antidepressants were included, with each drug considered as a separate arm indexed with a start date. Events were defined as the first occurrence of a low plasma sodium measurement or a clinical diagnosis recorded for either hyponatremia or SIADH. Those who did not have events were censored at their last plasma sodium measurement. A total of 17,439 individuals were exposed to one of the eight antidepressants as monotherapy. The overall incidences for hyponatremia were 0.87% in the first 30 days and 10.5% in the first 3 years in the antidepressant arms. Compared to sertraline, duloxetine (hazard ratio [HR] = 1.37 [1.19-1.58]) and escitalopram (HR = 1.16 [1.01-1.33]) were associated with the highest overall risk of hyponatremia, and bupropion (HR = 0.83 [0.73-0.94]) and paroxetine (HR = 0.78 [0.65-0.93]) were associated with the lowest risk. The risks were unchanged after adjusting for comorbidity and polypharmacy. Such information could help guide providers in managing patients and their risks of hyponatremia when on common antidepressants.
Published 2024. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no competing interests in this work.
Figures


References
-
- Mazhar, F. et al. Association of Hyponatraemia and Antidepressant Drugs: a pharmacovigilance‐pharmacodynamic assessment through an analysis of the US Food and Drug Administration adverse event reporting system (FAERS) database. CNS Drugs 33, 581–592 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Jacob, S. & Spinler, S.A. Hyponatremia associated with selective serotonin‐reuptake inhibitors in older adults. Ann. Pharmacother. 40, 1618–1622 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Nierenberg, A.A. , Ostacher, M.J. , Huffman, J.C. , Ametrano, R.M. , Fava, M. & Perlis, R.H. A brief review of antidepressant efficacy, effectiveness, indications, and usage for major depressive disorder. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 50, 428–436 (2008). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 1 OT2 OD025276/Community Partners
- HHSN 263201600085 U/Federally Qualified Health Centers
- 1 OT2 OD026551/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 1 OT2 OD 026552/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 1 U24 OD023163/Participant Technology Systems Center
- OT2 OD026555/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- 1 OT2 OD026557/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 1 OT2 OD026553/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- OT2 OD023206/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- 1 U24 OD023121/Biobank
- U24 OD023176/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- 1 OT2 OD026550/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 1 OT2 OD026549/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 5 U2C OD023196/Data and Research Center
- 1 OT2 OD026554/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 1 OT2 OD026548/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U2C OD023196/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- HG200417/ZIA
- 3 OT2 OD023206/Communications and Engagement
- U24 OD023121/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- HG200420/ZIC
- 1 OT2 OD026556/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- 3 OT2 OD025315/Community Partners
- U24 OD023176/CD/ODCDC CDC HHS/United States
- 3 OT2 OD023205/Communications and Engagement
- OT2 OD025276/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- 1 OT2 OD025277/Community Partners
- 1 OT2 OD025337/Community Partners
- 1 OT2 OD026555/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA HG200417/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U24 OD023163/OD/NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

