The role of co-occurring conditions and genetics in the associations of eating disorders with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder
- PMID: 39543370
- PMCID: PMC12014370
- DOI: 10.1038/s41380-024-02825-w
The role of co-occurring conditions and genetics in the associations of eating disorders with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder
Abstract
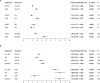
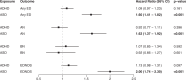
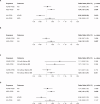
Eating disorders (EDs) commonly co-occur with other psychiatric and neurodevelopmental disorders including attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD); however, the pattern of family history and genetic overlap among them requires clarification. This study investigated the diagnostic, familial, and genetic associations of EDs with ADHD and ASD. The nationwide population-based cohort study included all individuals born in Denmark, 1981-2008, linked to their siblings and cousins. Cox regression was used to estimate associations between EDs and ADHD or ASD, and mediation analysis was used to assess the effects of intermediate mood or anxiety disorders. Polygenic scores (PGSs) were used to investigate the genetic association between anorexia nervosa (AN) and ADHD or ASD. Significantly increased risk for any ED was observed following an ADHD or ASD diagnosis. Mediation analysis suggested that intermediate mood or anxiety disorders could account for 44%-100% of the association between ADHD or ASD and ED. Individuals with a full sibling or maternal half sibling with ASD had increased risk of AN compared to those with siblings without ASD. A positive association was found between ASD-PGS and AN risk whereas a negative association was found between AN-PGS and ADHD. In this study, positive phenotypic associations between EDs and ADHD or ASD, mediation by mood or anxiety disorder, and genetic associations between ASD-PGS and AN and between AN-PGS and ADHD were observed. These findings could guide future research in the development of new treatments that can mitigate the development of EDs among individuals with ADHD or ASD.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: CMB is an author and royalty recipient from Pearson. DD has received speaker fees from Medici Nordic. The remaining authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Update of
-
The role of co-occurring conditions and genetics in the associations of eating disorders with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and autism spectrum disorder.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 17:rs.3.rs-4236554. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4236554/v1. Res Sq. 2024. Update in: Mol Psychiatry. 2025 May;30(5):2127-2136. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02825-w. PMID: 39070652 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH124851/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R335-2019-2339/Lundbeckfonden (Lundbeck Foundation)
- R01MH124871/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- R56MH129437/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- R344-2020-1060/Lundbeckfonden (Lundbeck Foundation)
- R01MH118278/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- R01 MH118278/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH120170/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- R276-2018-4581/Lundbeckfonden (Lundbeck Foundation)
- 538-2013-8864/Svenska Forskningsrådet Formas (Swedish Research Council Formas)
- R56 MH129437/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- 1052-00029B/Det Frie Forskningsråd (Danish Council for Independent Research)
- NNF21SA0072102/Novo Nordisk Fonden (Novo Nordisk Foundation)
- R01 MH119084/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- NNF20OC0065561/Novo Nordisk Fonden (Novo Nordisk Foundation)
- R01 MH120170/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH109514/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01MH119084/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | NIH | National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH)
- R248-2017-2003/Lundbeckfonden (Lundbeck Foundation)
- NNF20OC0064993/Novo Nordisk Fonden (Novo Nordisk Foundation)
- R102-A9118/Lundbeckfonden (Lundbeck Foundation)
- R01 MH124871/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- Niels Bohr Professorship/Danmarks Grundforskningsfond (Danish National Research Foundation)
- 965381/EC | Horizon 2020 Framework Programme (EU Framework Programme for Research and Innovation H2020)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

