Cardiac arrhythmias during and after thoracic irradiation for malignancies
- PMID: 39543778
- PMCID: PMC11562486
- DOI: 10.1186/s40959-024-00277-3
Cardiac arrhythmias during and after thoracic irradiation for malignancies
Abstract
Background: Cardiac arrhythmia has been reported as a significant complication of thoracic radiotherapy. Both bradyarrhythmias and tachyarrhythmias have been reported, highlighting the arrhythmia-modulating potential of radiation in certain oncologic therapies. This study aimed to analyse the arrhythmic burden in patients with cardiac implantable electrical devices (CIEDs) undergoing thoracic irradiation, examining both immediate effects of radiotherapy and long-term sequelae post-therapy.
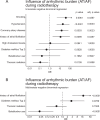
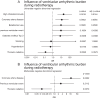
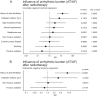
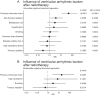
Methods and results: A retrospective cohort study was conducted involving patients with CIEDs who received thoracic radiotherapy between January 2012 and December 2022. Two distinct analyses were performed involving (1) daily CIED follow-ups during radiotherapy and (2) long-term arrhythmic outcomes post-therapy. For long-term outcomes, Patients were matched in a 1:2 ratio with non-irradiated controls based on age, sex, cardiovascular risk factors, cardiac disease, and beta-blocker use. Statistical analyses included negative binomial regression and propensity score matching. A total of 186 patients underwent daily CIED monitoring during radiotherapy, with 79 receiving thoracic irradiation. Thoracic irradiation was negatively associated with atrial arrhythmia (OR 0.11 [0.02;0.70, 95% CI], adjusted p = 0.0498) and there was a tendency towards less ventricular events (OR 0.14 [0.02;1.41, 95% CI], adjusted p = 0.3572) during radiotherapy in a univariate regression analysis. This association was not significant in the multivariate (OR 0.44 [0.10;1.80, 95%-CI], p = 0.16) model including a history of atrial fibrillation, diabetes and beta-blocker use. Coronary artery disease was associated with an increase in atrial and ventricular arrhythmia. For the long-term analysis, 122 patients were followed up after thoracic (N = 33) and non-thoracic radiation (N = 89) and compared to 244 matched controls drawn from approximately 10.000 CIED-patients. There was no significant increase in arrhythmic events compared to controls over a median follow-up of 6.6 months. A previous history of ventricular or atrial arrhythmic events was the strongest predictor for events during the follow-up.
Conclusion: Thoracic radiotherapy can be safely administered in patients with CIEDs. However, patients with a history of arrhythmia are more prone to arrhythmic events during and after radiation. These findings highlight the need for personalized arrhythmia management strategies and further research to understand the mechanisms underlying the antiarrhythmic effects of thoracic radiation.
Keywords: Cardiac arrhythmia; Cardiac implantable electrical devices; Cardiovascular toxicity; Radiation-induced heart disease; Radiotherapy; Thoracic radiation.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kocarnik JM, Compton K, Dean FE, Fu W, Gaw BL, Harvey JD, et al. Cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life years for 29 cancer groups from 2010 to 2019: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2019. JAMA Oncol. 2022;8:420–44. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34967848/. [Cited 2024 Jun 1]. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Miller KD, Nogueira L, Devasia T, Mariotto AB, Yabroff KR, Jemal A, et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 2022;72:409–36. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35736631/. [Cited 2024 Jun 1]. - PubMed
-
- McLaughlin PY, Kong W, de Metz C, Hanna TP, Brundage M, Warde P, et al. Do radiation oncology outreach clinics affect the use of radiotherapy? Radiother Oncol. 2018;127:143–9. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29478762/. [ Cited 2024 Jun 1]. - PubMed
-
- Delaney G, Jacob S, Featherstone C, Barton M. The role of radiotherapy in cancer treatment: estimating optimal utilization from a review of evidence-based clinical guidelines. Cancer. 2005;104:1129–37. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16080176/. [ Cited 2024 Jun 1]. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
