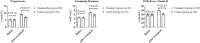Effect of vitamin D adjuvant therapy on the proportion of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood and pregnancy outcome of patients with recurrent miscarriage
- PMID: 39543837
- PMCID: PMC11635183
- DOI: 10.1111/jog.16151
Effect of vitamin D adjuvant therapy on the proportion of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood and pregnancy outcome of patients with recurrent miscarriage
Abstract
Background: Recurrent miscarriage (RM) is influenced by immune factors, particularly regulatory T cells, which can impact immune function and miscarriage risk. Vitamin D (VD) is known to regulate the immune system, potentially improving pregnancy outcomes in RM patients. This study aims to assess the effect of VD adjuvant therapy on regulatory T cells and pregnancy outcomes in RM patients.
Methods: Clinical data from 104 individuals with RM admitted to our hospital between March 2022 and February 2023 were allocated at random to either the VD group (VDG) or the control group (CG), with 52 patients in each group. Both groups received standard treatment; the CG was treated with aspirin, while the VDG received additional VD therapy. Outcomes measured included regulatory T cell proportion, metabolic factors, immune inflammatory markers, and pregnancy outcomes.
Results: After treatment, the proportion of regulatory T cells in VDG was considerably higher (p < 0.05). Additionally, triglyceride levels, leptin, fasting blood glucose, and fasting insulin were lower in the VDG, whereas adiponectin levels were higher (p < 0.05). Levels of progesterone, luteinizing hormone, and 25-hydroxy VD were also higher in the VDG (p < 0.05). Furthermore, interleukin-17, gamma interferon, tumor necrosis factor-α, and C-reactive protein were lower in the VDG (p < 0.05). The pregnancy success rate in the VDG was higher, and the preterm birth rate was lower (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Adjuvant treatment with VD can increase the proportion of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood of individuals with recurrent abortion, regulate metabolic disorder, alleviate immune inflammation, and improve pregnancy outcome.
Keywords: adjuvant therapy; pregnancy outcome; recurrent miscarriage; regulatory T cells; vitamin D.
© 2024 The Author(s). Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japan Society of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials