Survey of Experts' Opinions on the Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms
- PMID: 39543866
- PMCID: PMC11604339
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2024.0626
Survey of Experts' Opinions on the Diagnosis and Management of Pancreatic Cystic Neoplasms
Abstract
Objective: To survey experts' opinions in abdominal radiology (radiologists) and pancreas-specialized gastroenterology (pancreatologists) in South Korea regarding diagnosing and managing pancreatic cystic neoplasms (PCNs).
Materials and methods: Between August 25, 2023, and October 5, 2023, an online survey was conducted among members of the Korean Society of Abdominal Radiology and the Korean Pancreatobiliary Association via email invitation.
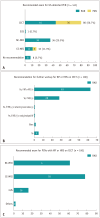
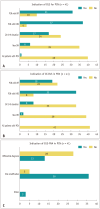
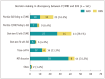
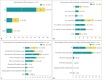
Results: The responses from 100 radiologists and 41 pancreatologists were analyzed. Of the respondents, 55.3% (78/141) reported seeing more than 50 patients or reading more than 50 exams related to PCN each month. The most common and preferred diagnostic modality for PCN was contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT), favored by 87.8% (36/41) of pancreatologists. When discrepancies arose between CECT or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and endoscopic ultrasound, 31.2% (44/141) of the respondents opted for multidisciplinary team discussion, whereas 29.1% (41/141) chose short-term follow-up using CECT or MRI. A total of 88.7% (125/141) of the respondents adhered to the 2017 International Association of Pancreatology (IAP) guidelines in their practice. Among the radiologists, 51.0% (51/100) endorsed a cut-off value of 5 mm for enhancing mural nodules, and 22.0% (22/100) supported a 5 mm/2 yr growth rate in the IAP guidelines v.2017. Additionally, 73.0% (73/100) of radiologists favored discontinuing surveillance, whereas 41.5% (17/41) of pancreatologists disagreed with stopping surveillance.
Conclusion: The survey underscores the clinical burden PCN poses and identifies CECT as the foremost diagnostic tool. Variability was noted in the terminology, differential diagnosis, approaches for resolving discrepancies between imaging examinations, and opinions on surveillance discontinuation among the respondents as a whole, as well as between radiologists and pancreatologists. Although the 2017 IAP guidelines are primarily followed, there remains a level of dissatisfaction with risk stratification among radiologists. This highlights the need for more standardized diagnostic algorithms and improved consensus among specialists to address these challenges.
Keywords: Consensus; Cyst; Guideline; Imaging; Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; Pancreas; Pancreatic cystic neoplasm; Recommendation; Surveillance.
Copyright © 2024 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Jeong Min Lee, who holds respective positions on the Editorial Board Member of the
Figures
Comment in
-
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine-Needle Aspiration for Pancreatic Cysts >2.5 cm Without Worrisome Features or High-Risk Stigmata.Korean J Radiol. 2025 Mar;26(3):281-282. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2024.1301. Korean J Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39999969 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Choi SH, Park SH, Kim KW, Lee JY, Lee SS. Progression of unresected intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas to cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;15:1509–1520.e4. - PubMed
-
- Elta GH, Enestvedt BK, Sauer BG, Lennon AM. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis and management of pancreatic cysts. Am J Gastroenterol. 2018;113:464–479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

