Chondroitin Sulfate-Coated Heteroduplex-Molecular Spherical Nucleic Acids
- PMID: 39544138
- PMCID: PMC11907394
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202400908
Chondroitin Sulfate-Coated Heteroduplex-Molecular Spherical Nucleic Acids
Abstract
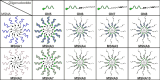
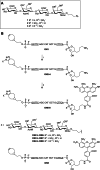
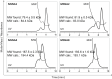
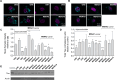
Molecular Spherical Nucleic Acids (MSNAs) are atomically uniform dendritic nanostructures and potential delivery vehicles for oligonucleotides. The radial formulation combined with covalent conjugation may hide the oligonucleotide content and simultaneously enhance the role of appropriate conjugate groups on the outer sphere. The conjugate halo may be modulated to affect the delivery properties of the MSNAs. In the present study, [60]fullerene-based molecular spherical nucleic acids, consisting of a 2'-deoxyribonucleotide and a ribonucleotide sequence, were used as hybridization-mediated carriers ("DNA and RNA-carriers") for an antisense oligonucleotide, suppressing Tau protein, (i. e. Tau-ASO) and its conjugates with chondroitin sulfate tetrasaccharides (CS) with different sulfation patterns. The impact of the MSNA carriers, CS-moieties on the conjugates and the CS-decorations on the MSNAs on cellular uptake and - activity (Tau-suppression) of the Tau-ASO was studied with hippocampal neurons in vitro. The formation and stability of these heteroduplex ASO-MSNAs were evaluated by UV melting profile analysis, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), dynamic light scattering (DLS) and size exclusion chromatography equipped with a multi angle light scattering detector (SEC-MALS). The cellular uptake and - activity were studied by confocal microscopy and Western blot analysis, respectively.
Keywords: Chondroitin sulfates; Drug Delivery; Heteroduplex ASOs; Molecular Spherical Nucleic Acids; Nanoparticles.
© 2024 The Author(s). ChemBioChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mirkin C. A., Letsinger R. L., Mucic R. C., Storhoff J. J., Nature 1996, 382(6592), 607–609. - PubMed
-
- Cutler J. I., Auyeung E., Mirkin C. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134(3), 1376–1391. - PubMed
-
- Rosi N. L., Giljohann D. A., Thaxton C. S., Lytton-Jean A. K. R., Han M. S., Mirkin C. A., Science 2006, 312(5776), 1027–1030. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

