Fluoride release and flexural strength of four ion-releasing restorative materials: An in vitro comparative study
- PMID: 39544218
- PMCID: PMC11559120
- DOI: 10.4317/jced.61818
Fluoride release and flexural strength of four ion-releasing restorative materials: An in vitro comparative study
Abstract
Background: This study aimed to determine the fluoride release and flexural strength of four ion-releasing restorative materials.
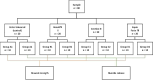
Material and methods: A total of 80 samples of four different materials were prepared in standardized molds: Ketac Universal, Beautifil II, Cention N, and Equia Forte Fil. The fluoride release was quantified at 1, 3, 7, 14, and 28 days post-immersion using an ion-selective electrode. The flexural strength was measured with a universal testing machine after 7 days of immersion in deionized water. A one-factor intergroup ANOVA with Welch's robust variance and Games-Howell's post hoc was employed. To compare related measures, a Friedman test with Bonferroni's adjusted post hoc was employed. The p-value was set at 0.05.
Results: At 7 days, significant differences were observed in the flexural strength of the four ion-releasing restorative materials (p<0.001). The flexural strength values from highest to lowest were as follows: Cention N (97.10 ± 4.99 MPa), Beautifil (82.77 ± 5.30 MPa), Equia Forte Fil (31.38 ± 7.68 MPa), and Ketac Universal (19.23 ± 2.94 MPa). In addition, at 3 and 7 days, the highest amount of fluoride released was observed for Cention N compared to the other ion-releasing restorative materials (p<0.05). Conversely, Beautifil II released the lowest amount of fluoride at 3, 7, 14, and 28 days (p<0.05) compared to the other ion-releasing restorative materials.
Conclusions: The immersion of all ion-releasing restorative materials in deionized water for seven days resulted in significant differences in flexural strength. Cention N had the highest value, while Ketac Universal had the lowest. All ion-releasing restorative materials released fluoride at all test times, with Ketac Universal releasing the most at 1, 14, and 28 days, and Cention N releasing it at 3 and 7 days. Beautifil II showed the lowest fluoride release at all evaluated times, exhibiting a nearly constant release over time compared to the other materials. Key words:Fluoride release, flexural strength, glass ionomer.
Copyright: © 2024 Medicina Oral S.L.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparative evaluation of the physical properties of a reinforced glass ionomer dental restorative material.J Prosthet Dent. 2019 Aug;122(2):154-159. doi: 10.1016/j.prosdent.2019.03.012. Epub 2019 Jul 17. J Prosthet Dent. 2019. PMID: 31326149
-
In-vitro evaluation of the shear bond strength and fluoride release of a new bioactive dental composite material.J Clin Exp Dent. 2022 Jan 1;14(1):e55-e63. doi: 10.4317/jced.58966. eCollection 2022 Jan. J Clin Exp Dent. 2022. PMID: 35070125 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Fluoride Release from Ion- Releasing Dental Materials.Acta Stomatol Croat. 2023 Sep;57(3):229-237. doi: 10.15644/asc57/3/3. Acta Stomatol Croat. 2023. PMID: 37808411 Free PMC article.
-
An In Vitro Evaluation of the Mechanical Properties and Fluoride-releasing Ability of a New Self-cure Filling Material.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2021 Feb 1;22(2):134-139. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2021. PMID: 34257171
-
Evaluation of F, Ca, and P release and microhardness of eleven ion-leaching restorative materials and the recharge efficacy using a new Ca/P containing fluoride varnish.J Dent. 2020 Nov;102:103474. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2020.103474. Epub 2020 Sep 14. J Dent. 2020. PMID: 32941973
References
-
- Cayo-Rojas CF, Gerónimo-Nieto EC, Aliaga-Mariñas AS. Salivary pH changes caused by cariogenic and non-cariogenic food intake in preschoolers from Huaura, Peru. Rev Cuba Estomatol. 2021;58(4):e3518.
-
- Cayo-Rojas CF, Santillán-Espadín KR, Nicho-Valladares MK, Ladera-Castañeda MI, Aliaga-Mariñas AS, Cervantes-Ganoza LA. Knowledge about oral health, salivary PH, body mass index and its relationship with dental caries in preschool children. Rev Fac Med. 2021;69(4):e88709.
-
- Allen-Revoredo C, Ladera-Castañeda M, Córdova-Limaylla N, Briceño-Vergel G, Cervantes-Ganoza L, Cayo-Rojas C. Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices on Oral Health Prevention Associated with Sociodemographic Factors of Adolescent Students from a Peruvian-Swiss Educational Institution. J Int Oral Health. 2022;14(5):475–486.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
