Guideline for the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Fatty Liver Disease (Version 2024)
- PMID: 39544247
- PMCID: PMC11557364
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2024.00311
Guideline for the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-associated Fatty Liver Disease (Version 2024)
Abstract
With the rising epidemic of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes mellitus in China, metabolic dysfunction-associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease has become the most prevalent chronic liver disease. This condition frequently occurs in Chinese patients with alcoholic liver disease and chronic hepatitis B. To address the impending public health crisis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its underlying metabolic issues, the Chinese Society of Hepatology and the Chinese Medical Association convened a panel of clinical experts to revise and update the "Guideline of prevention and treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (2018, China)". The new edition, titled "Guideline for the prevention and treatment of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (Version 2024)", offers comprehensive recommendations on key clinical issues, including screening and monitoring, diagnosis and evaluation, treatment, and follow-up for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease is now the preferred English term and is used interchangeably with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease. Additionally, the guideline emphasizes the importance of multidisciplinary collaboration among hepatologists and other specialists to manage cardiometabolic disorders and liver disease effectively.
Keywords: Cardiovascular disease; Guideline; Management; Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease; Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2024 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
JGF has been an Associate Editor of Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology since 2013. YMN has been an Editorial Board Member of Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology since 2022. JDJ and LW have been Executive Associate Editors of Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology since 2013. CS has been an Editorial Board Member of Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology since 2020. JL has been an Editorial Board Member of Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology since 2024. The other authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures
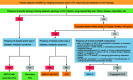
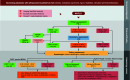

References
-
- National Workshop on Fatty Liver and Alcoholic Liver Disease, Chinese Society of Hepatology, Chinese Medical Association, Fatty Liver Expert Committee, Chinese Medical Doctor Association [Guidelines of prevention and treatment for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a 2018 update] Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2018;26(3):195–203. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2018.03.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD), European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO) EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) J Hepatol. 2024;81(3):492–542. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2024.04.031. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
