Myosteatosis: diagnostic significance and assessment by imaging approaches
- PMID: 39544479
- PMCID: PMC11558492
- DOI: 10.21037/qims-24-365
Myosteatosis: diagnostic significance and assessment by imaging approaches
Abstract
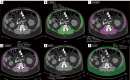
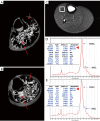
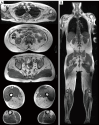
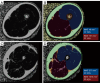
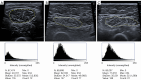
Myosteatosis has emerged as an important concept in muscle health as it is associated with an increased risk of adverse health outcomes, a higher rate of complications, and increased mortality associated with ageing, chronic systemic and neuromuscular diseases, cancer, metabolic syndromes, degenerative events, and trauma. Myosteatosis involves ectopic infiltration of fat into skeletal muscle, and it exhibits a negative correlation with muscle mass, strength, and mobility representing a contributing factor to decreased muscle quality. While myosteatosis serves as an additional biomarker for sarcopenia, cachexia, and metabolic syndromes, it is not synonymous with sarcopenia. Myosteatosis induces proinflammatory changes that contribute to decreased muscle function, compromise mitochondrial function, and increase inflammatory response in muscles. Imaging techniques such as computed tomography (CT), particularly opportunistic abdominal CT scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), have been used in both clinical practice and research. And in recent years, ultrasound has emerged as a promising bedside tool for measuring changes in muscle tissue. Various techniques, including CT-based muscle attenuation (MA) and intermuscular adipose tissue (IMAT) quantification, MRI-based proton density fat fraction (PDFF) and T1-T2 mapping, and musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS)-based echo intensity (EI) and shear wave elastography (SWE), are accessible in clinical practice and can be used as adjunct biomarkers of myosteatosis to assess various debilitating muscle health conditions. However, a stan¬dard definition of myosteatosis with a thorough understanding of the pathophysiological mechanisms, and a consensus in assessment methods and clinical outcomes has not yet been established. Recent developments in image acquisition and quantification have attempted to develop an appropriate muscle quality index for the assessment of myosteatosis. Additionally, emerging studies on artificial intelligence (AI) may provide further insights into quantification and automated assessment, including MRS analysis. In this review, we discuss the pathophysiological aspects of myosteatosis, all the current imaging techniques and recent advances in imaging assessment as potential biomarkers of myosteatosis, and the most common clinical conditions involved.
Keywords: Myosteatosis; computed tomography (CT); imaging biomarkers; magnetic resonance (MR); ultrasound (US).
2024 AME Publishing Company. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://qims.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/qims-24-365/coif). The special issue “Advances in Diagnostic Musculoskeletal Imaging and Image-guided Therapy” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. X.T. served as the unpaid Guest Editor of the issue. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie Y, Bruyère O, Cederholm T, Cooper C, Landi F, Rolland Y, Sayer AA, Schneider SM, Sieber CC, Topinkova E, Vandewoude M, Visser M, Zamboni M; Writing Group for the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People 2 (EWGSOP2), and the Extended Group for EWGSOP2. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing 2019;48:601. 10.1093/ageing/afz046 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Correa-de-Araujo R, Addison O, Miljkovic I, Goodpaster BH, Bergman BC, Clark RV, Elena JW, Esser KA, Ferrucci L, Harris-Love MO, Kritchevsky SB, Lorbergs A, Shepherd JA, Shulman GI, Rosen CJ. Myosteatosis in the Context of Skeletal Muscle Function Deficit: An Interdisciplinary Workshop at the National Institute on Aging. Front Physiol 2020;11:963. 10.3389/fphys.2020.00963 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
