Effect of FOLFOX regimen combined with cetuximab treatment on the efficacy and tumor markers of advanced colon cancer patients
- PMID: 39544802
- PMCID: PMC11558370
- DOI: 10.62347/KENB9486
Effect of FOLFOX regimen combined with cetuximab treatment on the efficacy and tumor markers of advanced colon cancer patients
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of FOLFOX regimen combined with cetuximab in the treatment of advanced colon cancer.
Methods: This retrospective study involved 60 patients with primary colon cancer who were treated in the PLA Navy Anqing Hospital from January 2022 to February 2023. According to their treatment regimen, the patients were divided into a treatment group that received FOLFOX4 combined with cetuximab (n=30), and a control group treated with cetuximab alone (n=30). The general data of the two groups were compared, and the short-term response rate was assessed by comparing the proportions of complete remission (CR), partial remission (PR), stable disease (SD) and progressive disease (PD) between the two groups. In addition, the progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were compared between the two groups, along with the adverse reactions and changes in serum tumor marker (CEA and CA19-9) levels.
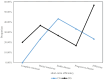
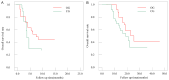
Result: The observation group showed a significantly higher short-term effective rate (CR+PR) compared to the control group (56.67% vs. 23.33%). The PFS and OS of the observation group were markedly longer compared to the control group. In terms of adverse reactions, the incidence of neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea was similar between the two groups; however, the incidence of rash in the observation group was higher. After the treatment, the serum CEA and CA19-9 levels decreased markedly in both groups, and the observation group demonstrated obviously lower levels than the control group (P<0.001). Similarly, the decreases in VEGF-A and VEGFR2 levels in the observation group were more significant than those in the control group (all P<0.001).
Conclusion: Despite inducing rash, which is controllable, the combined therapy of FOLFOX and cetuximab significantly improves short-term efficacy, reduces the levels of CEA, CA19-9, VEGF-A and VEGFR2, and extends the PFS and OS of patients, which can be served as an effective treatment strategy for advanced colon cancer.
Keywords: FOLFOX regimen; advanced colorectal cancer; cetuximab; tumor markers.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Serum CEA and CA19-9 in Efficacy Evaluations and Progression-Free Survival Predictions for Patients Treated with Cetuximab Combined with FOLFOX4 or FOLFIRI as a First-Line Treatment for Advanced Colorectal Cancer.Dis Markers. 2019 Jan 20;2019:6812045. doi: 10.1155/2019/6812045. eCollection 2019. Dis Markers. 2019. PMID: 30805037 Free PMC article.
-
Selective Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor Inhibitors Provide Limited Benefits for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(26):3171-3186. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200218095932. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32067605
-
Retrospective efficacy analysis of olaparib combined with bevacizumab in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023 May 27;15(5):906-916. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i5.906. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023. PMID: 37342840 Free PMC article.
-
FOLFOX plus anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) monoclonal antibody (mAb) is an effective first-line treatment for patients with RAS-wild left-sided metastatic colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Mar;97(10):e0097. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000010097. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 29517682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overall survival of patients with KRAS wild-type tumor treated with FOLFOX/FORFIRI±cetuximab as the first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Mar;96(12):e6335. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006335. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28328812 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- de Vries NL, van de Haar J, Veninga V, Chalabi M, Ijsselsteijn ME, van der Ploeg M, van den Bulk J, Ruano D, van den Berg JG, Haanen JB, Zeverijn LJ, Geurts BS, de Wit GF, Battaglia TW, Gelderblom H, Verheul HMW, Schumacher TN, Wessels LFA, Koning F, de Miranda NFCC, Voest EE. γδ T cells are effectors of immunotherapy in cancers with HLA class I defects. Nature. 2023;613:743–750. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zheng X, Ma S, Zhang Y, Lin W, Ji K, Wang C. In situ polymerization of fluorinated polyacrylate copolymer solid electrolytes for high-voltage lithium metal batteries at room temperature. Macromolecules. 2023;56:1077–1085.
-
- Taieb J, Puig PL, Bedenne L. Cetuximab plus FOLFOX-4 for fully resected stage III colon carcinoma: scientific background and the ongoing PETACC-8 trial. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2008;8:183–189. - PubMed
-
- Gallois C, Shi Q, Meyers JP, Iveson T, Alberts SR, de Gramont A, Sobrero AF, Haller DG, Oki E, Shields AF, Goldberg RM, Kerr R, Lonardi S, Yothers G, Kelly C, Boukovinas I, Labianca R, Sinicrope FA, Souglakos I, Yoshino T, Meyerhardt JA, Andre T, Papamichael D, Taieb J. Prognostic impact of early treatment and oxaliplatin discontinuation in patients with stage III colon cancer: an ACCENT/IDEA pooled analysis of 11 adjuvant trials. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023;41:803–815. - PubMed
-
- Xu JF, Li XY, Long L, Liu R. Enhancement of the physical and mechanical properties of wood using a novel organo-montmorillonite/hyperbranched polyacrylate emulsion. Holzforschung. 2021;75:545–554.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials