Effect of QingreHuoxue formula on Th17 cells and Tregs in mice with idiopathic membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 39544812
- PMCID: PMC11558394
- DOI: 10.62347/HJVG8103
Effect of QingreHuoxue formula on Th17 cells and Tregs in mice with idiopathic membranous nephropathy
Abstract
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate the therapeutic effect of the QingreHuoxue formula on mice with Idiopathic Membranous Nephropathy (IMN) and its impact on Th17 cells and Tregs.
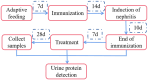
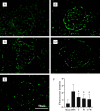
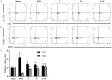
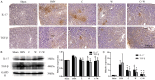
Methods: A mouse model of IMN was established, and the mice were treated with traditional Chinese medicine, western medicine, or a combination of both. The efficacy and immunomodulatory effects of the QingreHuoxue formula were evaluated by examining renal pathology, urinary protein levels, peripheral blood Th17 and Treg cell counts, and comparing the expression levels of IL-17 and transforming growth factor-β1 in renal tissues.
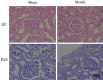
Results: Compared to the untreated IMN model group, the IMN mice treated with TCM, western medicine, or the combination showed significant improvements in proteinuria, renal pathology, peripheral T lymphocyte counts, and IL-17 expression in renal tissues. Notably, the group treated with a combination of Chinese and western medicine exhibited better outcomes than the group treated with western medicine alone.
Conclusions: The QingreHuoxue formula was effective in reducing proteinuria, modulating T cell immune function, and protecting renal tissue in mice with IMN.
Keywords: QingreHuoxue formula; idiopathic membranous nephropathy.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Traditional Chinese medicine for idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 31;10(7):e28836. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28836. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38596093 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Jian Pi Qu Shi Formula on intestinal bacterial flora in patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy: A prospective randomized controlled trial.Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2020 May 30;6(2):124-133. doi: 10.1016/j.cdtm.2020.04.004. eCollection 2020 Jun. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32596649 Free PMC article.
-
Renal outcomes of idiopathic and atypical membranous nephropathy in adult Chinese patients: a single center retrospective cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2021 Apr 22;22(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s12882-021-02348-4. BMC Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33888083 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Membranous Nephropathy in Western Countries.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2015 Sep;1(2):126-37. doi: 10.1159/000437287. Epub 2015 Sep 9. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2015. PMID: 27536673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Management of Membranous Nephropathy in Asia.Kidney Dis (Basel). 2015 Sep;1(2):119-25. doi: 10.1159/000437288. Epub 2015 Sep 1. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2015. PMID: 27536672 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hofstra JM, Wetzels JF. Introduction of a cyclophosphamide-based treatment strategy and the risk of ESRD in patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a nationwide survey in the Netherlands. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2008;23:3534–3538. - PubMed
-
- Liu D, Yang Y, Kuang F, Qing S, Hu B, Yu X. Risk of infection with different immunosuppressive drugs combined with glucocorticoids for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a pairwise and network meta-analysis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019;70:354–361. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
