Association between hip fracture fixation methods and bone mineral density T-value in middle-aged and elderly patients with hip fractures
- PMID: 39544814
- PMCID: PMC11558412
- DOI: 10.62347/ZNRF6159
Association between hip fracture fixation methods and bone mineral density T-value in middle-aged and elderly patients with hip fractures
Abstract
Objective: To examine the association of proximal femoral nail anti-rotation (PFNA) and dynamic hip screw (DHS) with bone mineral density T-value (BMDT) in middle-aged and elderly patients suffering from hip fractures.
Methods: Clinical data were collected from 110 patients with hip fractures who underwent internal fixation surgery between October 2020 and June 2021. Patients treated with DHS were included in the control group, and those treated with PFNA were classified into the observation group. The disparity in BMDT between the two groups was assessed. Patients were further divided into two groups based on the median BMDT at 6 months post-surgery: a high BMDT group (BMDT>-1.1 SD) and a low BMDT group (BMDT≤-1.1 SD). Factors influencing BMDT were analyzed.
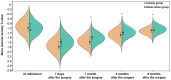
Results: Repeated measures ANOVA showed that BMDT in the observation group was higher than that in the control group at 7 days, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months after the surgery (between-group effect: F=258.400, P<0.001). BMDT in both groups increased with time but remained lower than pre-surgery levels (time effect: F=28.760, P<0.001), with an interaction between group and time (F=6.478, P<0.05). Correlation analysis showed a significant correlation between internal fixation techniques and BMDT at 7 days, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months after the surgery (P<0.05). Logistic regression analysis showed that advanced age and a higher VAS score at 72 hours post-surgery were risk factors for low BMDT at 6 months post-surgery, while PFNA was a protective factor (all P<0.05).
Conclusion: Compared to DHS, PFNA significantly improves BMDT in middle-aged and elderly patients following hip fracture surgery, promoting better early-stage recovery. PFNA should be prioritized in clinical practice to enhance postoperative outcomes.
Keywords: Middle-aged patients; bone mineral density T-value; correlation; elderly patients; hip fracture; internal fixation.
AJTR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Comparative study of proximal femoral nail anti-rotation and dynamic hip screw in the unstable intertrochanteric fractures in the elderly].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018 Jan 30;98(5):357-361. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2018.05.008. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2018. PMID: 29429246 Chinese.
-
Conversion to total hip arthroplasty after failed proximal femoral nail antirotations or dynamic hip screw fixations for stable intertrochanteric femur fractures: a retrospective study with a minimum follow-up of 3 years.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017 Jan 25;18(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12891-017-1415-6. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2017. PMID: 28122548 Free PMC article.
-
PFNA vs. DHS helical blade for elderly patients with osteoporotic femoral intertrochanteric fractures.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Jul;22(1 Suppl):1-7. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201807_15346. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30004570
-
Cephalomedullary nail versus sliding hip screw for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2013 Dec;21(3):308-12. doi: 10.1177/230949901302100309. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). 2013. PMID: 24366790
-
Antirotation proximal femoral nail versus dynamic hip screw for intertrochanteric fractures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013 Jun;99(4):377-83. doi: 10.1016/j.otsr.2012.12.019. Epub 2013 May 23. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2013. PMID: 23707739 Review.
References
-
- Zhang LZ, Gao J, Zhang ZC, Wang XW, Zhang JZ, Sun TS. Comparison of clinical effects of total artificial hip replacement and cannulated screw fixation for the treatment of displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2018;31:103–110. - PubMed
-
- Peng YL, Wang ZY, Wang XJ, Ji YT, Wen Y, Mai Y. Lower risk of low bone mineral density in high vitamin E level in older people: a cross-sectional study. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 2024;61:316–321. - PubMed
-
- Yu C, Jiang LH, Cai DW, Wu J, Qin J. PFNA and InterTAN intramedullary nailing in elderly patients with femoral intertrochanteric fractures: a Meta analysis. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2019;32:120–129. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
