Drug Survival, Retention, and Persistence of Dupilumab in Adults and Adolescents with Atopic Dermatitis: A Narrative Literature Review
- PMID: 39546252
- PMCID: PMC11782415
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-024-03052-z
Drug Survival, Retention, and Persistence of Dupilumab in Adults and Adolescents with Atopic Dermatitis: A Narrative Literature Review
Abstract
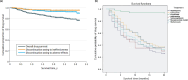
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a chronic, relapsing inflammatory skin condition that can have a negative impact on a patient's quality of life. Long-term effectiveness is required to manage the symptoms of AD (skin inflammation, eczematous lesions, and itching). Because some of the systemic immunosuppressants used to treat AD have been associated with serious adverse events (AEs), other safer, more effective options, including dupilumab, have been proven effective long-term for treatment of adult and adolescent patients with moderate-to-severe AD. The long-term safety and effectiveness of a drug are usually confirmed in real-world studies by evaluating its performance over time. Measures such as drug survival, drug retention, drug persistence, or retention rates reflect whether treatment may be considered as satisfactory by both patients and physicians, meeting key clinical needs. This review aimed to describe the survival, retention, or persistence of dupilumab therapy in adults and adolescents with moderate-to-severe AD by conducting a PubMed search in March 2023 and screening for relevant publications. Globally, real-world studies with dupilumab have regularly reported high drug survival rates after 1, 2, and 3 years of observation, being consistently at 80-90%, with low rates of treatment discontinuation due to lack of efficacy or AEs. These findings are notably higher than 1- and 2-year drug survival rates of systemic immunosuppressants (including cyclosporine [37% and 20%, respectively] and methotrexate [41% and 33%, respectively]). Overall, real-world data on drug survival have confirmed that dupilumab provides long-term sustained efficacy and acceptable safety in patients with moderate-to-severe AD.
Keywords: Atopic dermatitis; Drug survival; Dupilumab; Persistence; Retention.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Conflict of Interest: Mariateresa Rossi is a consultant, advisory board member, and speaker for Sanofi, Leo Pharma, AbbVie, Pfizer, and L’Oréal. Silvia M. Ferrucci was a principal investigator in clinical trials for AbbVie, Almirall, Galderma, Leo Pharma, Sanofi, Amgen, Novartis, and Bayer; and received honoraria for lectures from Novartis and Menarini. Piergiacomo Calzavara-Pinton has received personal fees as a consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Leo Pharma, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Cantabria, Molteni Farmaceutici, Galderma, La Roche Posay, Naos, Incyte, Celgene, and Sanofi, outside the present work. Angelo V. Marzano is on consultancy/advisory boards and received disease-relevant honoraria from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Pfizer, Sanofi, and UCB. Ketty Peris has received honoraria for advisory board and grants from AbbVie, Almirall, Biogen Celgene, Galderma, Leo Pharma, Lilly, Janssen, Novartis, Sanofi, and Sun Pharma, outside the submitted work. Elena Nicoli and Devis Moretti are employees of Sanofi and may hold shares and/or stock options in the company. Andrea Chiricozzi has received personal fees as a consultant, advisory board member, and/or speaker from AbbVie, Boehringer Ingelheim, Leo Pharma, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, and Sanofi. Ethical Approval: This article is based on previously conducted studies and does not contain any new studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Wollenberg A, Barbarot S, Bieber T, et al. Consensus-based European guidelines for treatment of atopic eczema (atopic dermatitis) in adults and children: part I. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:657–82. - PubMed
-
- Kulthanan K, Tuchinda P, Nitiyarom R, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atopic dermatitis. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. 2021;39:145–55. - PubMed
-
- Silverberg JI, Barbarot S, Gadkari A, et al. Atopic dermatitis in the pediatric population: a cross-sectional, international epidemiologic study. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021;126:417-28.e2. - PubMed
-
- Barbarot S, Auziere S, Gadkari A, et al. Epidemiology of atopic dermatitis in adults: results from an international survey. Allergy. 2018;73:1284–93. - PubMed
-
- Chrostowska-Plak D, Reich A, Szepietowski JC. Relationship between itch and psychological status of patients with atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:e239–42. - PubMed

