High mobility group A1 (HMGA1) promotes the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer by increasing lipid synthesis
- PMID: 39548107
- PMCID: PMC11568219
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-54400-0
High mobility group A1 (HMGA1) promotes the tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer by increasing lipid synthesis
Abstract
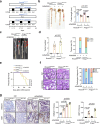
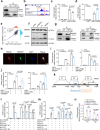
Metabolic reprogramming is a hallmark of cancer, enabling tumor cells to meet the high energy and biosynthetic demands required for their proliferation. High mobility group A1 (HMGA1) is a structural transcription factor and frequently overexpressed in human colorectal cancer (CRC). Here, we show that HMGA1 promotes CRC progression by driving lipid synthesis in a AOM/DSS-induced CRC mouse model. Using conditional knockout (Hmga1△IEC) and knock-in (Hmga1IEC-OE/+) mouse models, we demonstrate that HMGA1 enhances CRC cell proliferation and accelerates tumor development by upregulating fatty acid synthase (FASN). Mechanistically, HMGA1 increases the transcriptional activity of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1) on the FASN promoter, leading to increased lipid accumulation in intestinal epithelial cells. Moreover, a high-fat diet exacerbates CRC progression in Hmga1△IEC mice, while pharmacological inhibition of FASN by orlistat reduces tumor growth in Hmga1IEC-OE/+ mice. Our findings suggest that targeting lipid metabolism could offer a promising therapeutic strategy for CRC.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures






References
-
- Ye, L., Li, Y., Zhang, S., Wang, J. & Lei, B. Exosomes-regulated lipid metabolism in tumorigenesis and cancer progression. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.73, 27–39 (2023). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

