Phase angle is a useful predicting indicator for protein-energy wasting and cardiovascular risk among maintenance hemodialysis patients
- PMID: 39548164
- PMCID: PMC11568186
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-78957-4
Phase angle is a useful predicting indicator for protein-energy wasting and cardiovascular risk among maintenance hemodialysis patients
Abstract
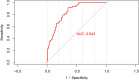
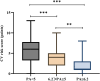
Protein-energy wasting (PEW) is a major contributor to the high mortality among maintenance hemodialysis (MHD) patients. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in dialysis patients, and PEW can significantly increase cardiovascular mortality in MHD patients. Previous studies have confirmed that PA may be a good objective indicator for determining the nutritional status and prognosis of MHD patients. Our study aimed to determine the predictive value of phase angle (PA) as detected by bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) on PEW and cardiovascular (CV) risk among MHD patients. Our retrospective observational study involved 161 adult patients with HD. The Cardiovascular risk score is a risk model based on the Japan Dialysis Outcome and Practice Patterns Study (J-DOPPS). We established LASSO logistic regression analysis model to identify key parameters related to body composition that can predict PEW in MHD patients. The area under the curve (AUC) values for PA, appendicular skeletal muscle mass index (ASMI), body cell mass (BCM), and mid-arm circumference (MAC) in predicting PEW in male MHD patients were relatively large, with 0.708, 0.674, 0.663, and 0.735, respectively. The predicted PEW values of these parameters were slightly lower in female patients than in men. We incorporated PA, ASMI, BCM, and MAC into a model that predicted the incidence of PEW in maintenance hemodialysis patients using LASSO technology. We discovered that the model predicted a greater AUC of PEW occurrence than any single factor, 0.877 for men and 0.76 for women. The results of the univariate logistic regression analysis showed that the low PA tertile array group had a greater incidence of PEW than the high PA group (P < 0.001). Additionally, we also found that lower PA was associated with higher CV risk scores. The PA detected by bioelectrical impedance analysis could predict the risk of PEW and cardiovascular events among patients with MHD. When used in conjunction, PA, ASMI, BCM, and MAC have a high diagnostic efficacy for PEW in patients on maintenance hemodialysis.
Keywords: Bioelectrical impedance analysis; Cardiovascular risk; Hemodialysis; Phase angle; Protein energy wasting.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis-Derived Phase Angle Predicts Protein-Energy Wasting in Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients.J Ren Nutr. 2019 Jul;29(4):295-301. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2018.09.001. Epub 2018 Nov 13. J Ren Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30446269
-
Bioelectrical impedance analysis-derived phase angle as a determinant of protein-energy wasting and frailty in maintenance hemodialysis patients: retrospective cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2020 Oct 19;21(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12882-020-02102-2. BMC Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 33076872 Free PMC article.
-
Associations between bioelectrical impedance analysis-derived phase angle, protein-energy wasting and all-cause mortality in older patients undergoing haemodialysis.Nephrology (Carlton). 2024 Oct;29(10):655-662. doi: 10.1111/nep.14333. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Nephrology (Carlton). 2024. PMID: 38858748
-
Protein-energy wasting and nutritional supplementation in patients with end-stage renal disease on hemodialysis.Clin Nutr. 2017 Jun;36(3):663-671. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.06.007. Epub 2016 Jun 18. Clin Nutr. 2017. PMID: 27371993 Review.
-
Managing protein-energy wasting in hemodialysis patients: A comparison of animal- and plant-based protein foods.Semin Dial. 2019 Jan;32(1):41-46. doi: 10.1111/sdi.12737. Epub 2018 Jul 15. Semin Dial. 2019. PMID: 30009545 Review.
References
-
- Nangaku, M. Global perspective of kidney diseases: Challenges and changes. Nephrology (Carlton).28(Suppl 1), 5–7 (2023). - PubMed
-
- Han, Q. et al. A high neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is associated with poor nutritional status in chronic kidney disease patients. Br .J. Nutr.128(10), 1990–1996 (2022). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

