Structural characteristics of plankton community in Dongting Lake and its relationship with water environmental factors
- PMID: 39548227
- PMCID: PMC11568284
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-024-79330-1
Structural characteristics of plankton community in Dongting Lake and its relationship with water environmental factors
Abstract
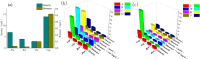
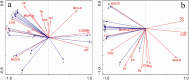
The plankton community structure and environmental factors in Dongting Lake were investigated during four seasons from September 2020 to August 2021. The results revealed 147 species from 58 genera and 7 phyla of phytoplankton and 84 species from 56 genera and 4 phyla of zooplankton in Dongting Lake. The characteristics of plankton communities varied with time and space. The temporal variation of phytoplankton abundance ranged from 43.5201 × 104 to 120.7968 × 104 cells/L and the spatial variation ranged from 18.6707 × 104 to 247.5542 × 104 cells/L. The temporal variation of zooplankton abundance ranged from 18 to 42 ind/L and the spatial variation ranged from 19 to 62 ind/L. The temporal and spatial variations of the abundance range values were much larger for phytoplankton than for zooplankton, with phytoplankton dominating. However, environmental factors in Dongting Lake vary more temporally than spatially, and drive more temporal than spatial variations in planktonic organisms. Based on the redundancy analysis WT, DO, and CODMn were the main environmental factors affecting the distribution of phytoplankton, while WT, CODMn, NO2-N, and Chl-a were the main factors affecting the distribution of zooplankton. WT and CODMn were the common key influencing factors.
Keywords: Dongting lake; Plankton; Redundancy analysis; Temporal and spatial variations; Water environmental factors.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures







Similar articles
-
Temporal variation in zooplankton and phytoplankton community species composition and the affecting factors in Lake Taihu-a large freshwater lake in China.Environ Pollut. 2019 Feb;245:1050-1057. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.11.007. Epub 2018 Nov 3. Environ Pollut. 2019. PMID: 30682739
-
[Characterization of the Ecological Niche and Interspecific Connectivity of Plankton in Baiyangdian Lake by Combining Ecological Networks].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2024 Sep 8;45(9):5298-5307. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202309195. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2024. PMID: 39323148 Chinese.
-
[Plankton Community Stability and Drive Factor Identification Guizhou Plateau Reservoir].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2024 Jul 8;45(7):3983-3994. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202307139. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2024. PMID: 39022946 Chinese.
-
[Structural Characteristics of Zooplankton and Phytoplankton Communities and Its Relationship with Environmental Factors in Different Regions of Nanhu Lake in Jiaxing City].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2022 Jun 8;43(6):3106-3117. doi: 10.13227/j.hjkx.202108011. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2022. PMID: 35686780 Chinese.
-
Ecology under lake ice.Ecol Lett. 2017 Jan;20(1):98-111. doi: 10.1111/ele.12699. Epub 2016 Nov 27. Ecol Lett. 2017. PMID: 27889953 Review.
References
-
- Badruzzaman, M. et al. Sources of nutrients impacting surface waters in Florida: A review. J. Environ. Manag.109, 80–92. 10.1016/j.jenvman.2012.04.040 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Zhang, X. J. et al. Effects of ecological protection and restoration on phytoplankton diversity in impounded lakes along the eastern route of China’s South - to - North Water Diversion Project. Sci. Tot. Environ.795, 148870. 10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2021.148870 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Echaniz, S. A. et al. Zooplankton seasonal abundance of south American saline shallow lakes. Int. Rev. Hydrobiol.91(1), 86–100. 10.1002/iroh.200510803 (2006).
-
- Amorim, C. A. & Moura, A. D. N. Ecological impacts of freshwater algal blooms on water quality, plankton biodiversity, structure, and ecosystem functioning. Sci. Tot. Environ.758, 143605. 10.1016/J.SCITOTENV.2020.143605 (2021). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

