Variations in inflammatory regulators in male patients with chronic schizophrenia associated with psychopathology and cognitive deficits
- PMID: 39548412
- PMCID: PMC11566147
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-024-06288-9
Variations in inflammatory regulators in male patients with chronic schizophrenia associated with psychopathology and cognitive deficits
Abstract
Background: Immune dysregulation has been identified as a contributing factor in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia. This study aimed to investigate variations in specific immune regulators and their correlation with psychopathology and cognitive functions in male patients with chronic schizophrenia.
Methods: Employing a cross-sectional design, this study included 72 male patients with chronic schizophrenia. The Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS) and the Repeatable Battery for the Assessment of Neuropsychological Status were utilized to assess psychopathology and cognitive functions, respectively.
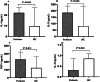
Results: Serum levels of interleukin (IL)-4, IL-10, IL-12p40, IL-13, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) were measured. There were significantly increased levels of IL-4, IL-13, and MCP-1, alongside decreased levels of IL-10 in patients compared to controls (all P < 0.05). IL-4 levels showed a significant negative association with PANSS positive symptoms (beta=-0.222, P = 0.042). After controlling for antipsychotic medication, BMI, and smoking, this correlation was no longer significant (r=-0.232, P = 0.055). Additionally, positive correlations of IL-4 (beta = 0.297, P = 0.008), IL-13 (beta = 0.371, P = 0.001), and MCP-1 (beta = 0.280, P = 0.013) with language scores were observed. Increased levels of IL-4 (P = 0.044, OR = 1.994), IL-13 (P = 0.019, OR = 2.245), as well as IL-4 and MCP-1 interactions (P = 0.043, OR = 2.000) were positively associated with the risk of chronic schizophrenia, while lower levels of IL-10 (P = 0.003, OR = 0.2.867) were also linked to an increased risk.
Conclusion: The identified associations between specific immune markers and the clinical and cognitive features of chronic schizophrenia in males underscored the potential immune-mediated mechanisms underlying schizophrenia.
Keywords: Cognitive deficits; Immune dysregulation; PANSS; RBANS; Schizophrenia.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Decreased plasma levels of gasotransmitter hydrogen sulfide in patients with schizophrenia: correlation with psychopathology and cognition.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Aug;235(8):2267-2274. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4923-7. Epub 2018 May 18. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29777287
-
Sex differences in the association of body mass index with symptoms and cognitive deficits in Chinese patients with chronic schizophrenia.Transl Psychiatry. 2020 Jan 21;10(1):18. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-0717-x. Transl Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32066717 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-3, symptoms and cognitive deficits in first-episode drug-naïve and chronic medicated schizophrenia.Psychiatry Res. 2018 May;263:147-153. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2018.02.054. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Psychiatry Res. 2018. PMID: 29554544
-
Altered interleukin-18 levels are associated with cognitive impairment in chronic schizophrenia.J Psychiatr Res. 2016 May;76:9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2016.01.013. Epub 2016 Jan 29. J Psychiatr Res. 2016. PMID: 26866662
-
Increased interleukin-2 serum levels were associated with psychopathological symptoms and cognitive deficits in treatment-resistant schizophrenia.Schizophr Res. 2015 Dec;169(1-3):16-21. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2015.10.038. Epub 2015 Nov 6. Schizophr Res. 2015. PMID: 26549630
References
-
- Velligan DI, Rao S. The Epidemiology and Global Burden of Schizophrenia. J Clin Psychiatry 2023, 84(1). - PubMed
-
- Huang Y, Wang Y, Wang H, Liu Z, Yu X, Yan J, Yu Y, Kou C, Xu X, Lu J, et al. Prevalence of mental disorders in China: a cross-sectional epidemiological study. Lancet Psychiatry. 2019;6(3):211–24. - PubMed
-
- Radua J, Ramella-Cravaro V, Ioannidis JPA, Reichenberg A, Phiphopthatsanee N, Amir T, Yenn Thoo H, Oliver D, Davies C, Morgan C, et al. What causes psychosis? An umbrella review of risk and protective factors. World Psychiatry: Official J World Psychiatric Association (WPA). 2018;17(1):49–66. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

