Highly Sensitive and Specific Panels of Plasma Exosomal microRNAs for Identification of Malignant Pulmonary Nodules
- PMID: 39548655
- PMCID: PMC11567941
- DOI: 10.1111/crj.70034
Highly Sensitive and Specific Panels of Plasma Exosomal microRNAs for Identification of Malignant Pulmonary Nodules
Abstract
Objectives: With wide application of computed tomography (CT) in early lung cancer screening, solitary pulmonary nodules (SPNs) are frequently detected. Due to their high etiological diversity and potential for malignancy, rapid and accurate identification and malignant SPNs are crucial in the clinical management. In the present study, plasma exosomal microRNAs were identified and evaluated as sensitive and specific indicators for malignant SPNs.
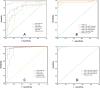
Materials and methods: Exosomal miRNAs isolated from the plasmas of pathologically confirmed patients with SPN (four malignant and four benign, designated as the screening set) were subjected for high throughput sequencing and eight candidate miRNAs were selected. The pre-operation plasma levels of the candidate miRNAs in 77 patients with SPN (48 malignant and 29 benign, designated as the identification set) were detected by quantitative PCR, five miRNAs were identified as potential biomarkers for malignant SPNs, and the diagnostic values of the five miRNAs each alone or combined were then analyzed by AUROC analysis. The prediction values of the identified miRNAs were further evaluated in 95 patients with SPN (double blind, 74 malignant and 21 benign, designated as the validation set).
Results: High-throughput sequencing identified 45 miRNAs with statistical differences between benign and malignant SPNs. Among the eight candidate miRNAs in the identification set, miR-1-3p alone had the best diagnostic value, with the sensitivities and specificities of 89.6% and 100% for malignant SPNs. Unexpectedly, when miR-1-3p was combined with miR-99a-5p, both the sensitivity and specificity reached 100% for malignant SPNs. miR-1-3p+miR-125b-5p and miR-1-3p+miR-218-5p were also good indicators of malignant SPNs with sensitivities of 95.8% and 97.9%, specificities of 100% and 96.6%. Further analysis of these microRNA combinations in the validation set indicated that the PPV were 91.4%, 97.4%, and 93.5% and the NPV were 100%, 100%, and 88.9% for miR-1-3p+miR-99a-5p, miR-1-3p+miR-218-5p, and miR-1-3p+miR-125b-5p, with the sensitivities were 100%, 100%, and 97.3% and the specificities were 66.7%, 90.5%, and 76.2% for miR-1-3p+miR-99a-5p, miR-1-3p+miR-218-5p, and miR-1-3p+miR-125b-5p, respectively.
Conclusions: Through high throughput sequencing, qPCR determination of plasma microRNAs and AUROC analysis, miR-1-3p combined with miR-99a-5p, miR-125b-5p, or miR-218-5p have been found to be sensitive and specific indicators of malignant SPNs in both the identification and validation sets. Our results indicate that the panels of plasma miRNAs can be used as diagnostic biomarkers for malignant SPNs.
Keywords: diagnostic biomarkers; early diagnosis; exosomal microRNAs; plasma; solitary pulmonary nodules.
© 2024 The Author(s). Clinical Respiratory Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Panels of miRNAs, i.e., miR‐1‐3p and miR‐99a‐5p, miR‐1‐3p and miR‐218‐5p, and miR‐1‐3p and miR‐125b‐5p, are applying national invention patents (Application numbers are 202111530540.7 and 202 111 530 337.X).
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diagnosis of lung cancer in individuals with solitary pulmonary nodules by plasma microRNA biomarkers.BMC Cancer. 2011 Aug 24;11:374. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-11-374. BMC Cancer. 2011. PMID: 21864403 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of exosomal miRNA biomarkers for diagnosis of papillary thyroid cancer by small RNA sequencing.Eur J Endocrinol. 2020 Jan;182(1):111-121. doi: 10.1530/EJE-19-0524. Eur J Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 31721725
-
Combining serum miRNAs, CEA, and CYFRA21-1 with imaging and clinical features to distinguish benign and malignant pulmonary nodules: a pilot study : Xianfeng Li et al.: Combining biomarker, imaging, and clinical features to distinguish pulmonary nodules.World J Surg Oncol. 2017 May 25;15(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12957-017-1171-y. World J Surg Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28545454 Free PMC article.
-
The diagnostic and prognostic value of exosomal microRNAs in lung cancer: a systematic review.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Aug;26(8):1921-1933. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03414-7. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38485857
-
The role of MicroRNAs as early biomarkers of asbestos-related lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pulmonology. 2025 Dec 31;31(1):2416792. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2024.02.002. Epub 2024 Oct 24. Pulmonology. 2025. PMID: 38402124
References
-
- Ettinger D. S., Aisner D. L., Wood D. E., et al., “NCCN Guidelines Insights: Non‐Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 5.2018,” Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network : JNCCN 16, no. 7 (2018): 807–821. - PubMed
-
- MacMahon H., Naidich D. P., Goo J. M., et al., “Guidelines for Management of Incidental Pulmonary Nodules Detected on CT Images: From the Fleischner Society 2017,” Radiology 284, no. 1 (2017): 228–243. - PubMed
-
- Cruickshank A., Stieler G., and Ameer F., “Evaluation of the Solitary Pulmonary Nodule,” Internal Medicine Journal 49, no. 3 (2019): 306–315. - PubMed
-
- Lesser T. G., Petersen I., Polzing F., and Wolfram F., “One‐Lung Flooding Enables Ultrasound‐Guided Transthoracic Needle Biopsy of Pulmonary Nodules With High Sensitivity,” Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology 44, no. 7 (2018): 1556–1562. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2021zhyx-c67/Research Fund of Anhui Institute of Translational Medicine
- KJ2021ZD0028/Natural Science Research Project of Anhui Universities
- 2208085MH194/Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province
- 2021zdynjb06/Collaborative Chinese and Western Medicine Research Project for Major Difficult Diseases
- 2021037/Hefei Municipal Natural Science Foundation
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

