Development of a habit-based intervention to support healthy eating and physical activity behaviours for pregnant women with overweight or obesity: Healthy Habits in Pregnancy and Beyond (HHIPBe)
- PMID: 39550532
- PMCID: PMC11568677
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-024-06945-7
Development of a habit-based intervention to support healthy eating and physical activity behaviours for pregnant women with overweight or obesity: Healthy Habits in Pregnancy and Beyond (HHIPBe)
Abstract
Background: The number of women entering pregnancy with overweight or obesity is increasing. This can increase the risk for excessive gestational weight gain (GWG) which is associated with health complications for mother and baby. There are limited evidence-based interventions within antenatal care settings to encourage healthy eating and physical activity behaviours and support women with managing GWG.
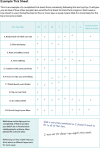
Methods: A previous habit-based intervention 'Ten Top Tips for a Healthy Weight' (10TT) was adapted and made suitable for pregnancy in line with the Medical Research Council's (MRC) complex intervention development guidelines. It involved three key activities: (1) identifying the evidence base; (2) identifying appropriate theory; and, (3) modelling processes. A core element was integrating lived experience via personal and public involvement (PPI).
Results: The original 10TTs were adapted with PPI in line with current advice on nutrition and physical activity in pregnancy. New intervention materials were devised, including a leaflet and a logbook and app for self-monitoring to be delivered alongside a brief 1:1 conversation. Behaviour change techniques (BCTs) included in the new materials were coded using a number of behavioural taxonomies. An E-learning resource was created to help standardise the approach to delivery of the intervention and avoid stigmatising conversations.
Conclusion: Following MRC guidance for the development of complex interventions alongside significant PPI allowed for the adaption of 10TT habit-based weight management intervention into the 'Healthy Habits in Pregnancy and Beyond' (HHIPBe) intervention. The feasibility and acceptability of implementing this intervention in the antenatal setting will be explored in a feasibility randomised controlled trial.
Trial registration: This study was registered on Clinical Trials as 'Healthy Habits in Pregnancy and Beyond (HHIPBe)' ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT04336878. The study was registered on 07/04/2020.
Keywords: Activity; Behaviour; Behavioural intervention; Diet; Gestational weight gain; Health; Intervention development; Obesity; Overweight; Personal and public involvement (PPI); Pregnancy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Zhao R, Xu L, Wu ML, Huang SH, Cao XJ. Maternal pre-pregnancy body mass index, gestational weight gain influence birth weight. Women Birth J Aust Coll Midwives. 2018;31:20–5 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28716548. - PubMed
-
- The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG). ACOG Committee Opinion. 2013 [cited 2018 Dec 11]. https://www.acog.org/Clinical-Guidance-and-Publications/Committee-Opinio....
-
- Shieh C, Cullen DL, Pike C, Pressler SJ. Intervention strategies for preventing excessive gestational weight gain: systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2018;19:1093–109. 10.1111/obr.12691. - PubMed
-
- Vincze L, Rollo M, Hutchesson M, Hauck Y, MacDonald-Wicks L, Wood L et al. Interventions including a nutrition component aimed at managing gestational weight gain or postpartum weight retention. JBI Database Syst Rev Implement Reports. 2019 [cited 2019 Mar 19];17:297–364. Available from: http://insights.ovid.com/crossref?an=01938924-201903000-00007. - PubMed

