Effectiveness of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) in the differentiation of thyroid nodules
- PMID: 39551736
- PMCID: PMC11571896
- DOI: 10.1186/s13044-024-00210-x
Effectiveness of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) in the differentiation of thyroid nodules
Abstract
Background: The aim was to investigate which of two different b values (b 500 s/mm² and b 800 s/mm²) are more effective in the differentiation of benign-malignant nodules using Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging (DW-MRI).
Materials and methods: Patients presenting with a preoperative diagnosis of nodular goiter or multinodular goiter were included in this study. These patients underwent neck MRI examinations, and their cases were analyzed retrospectively. A total of 26 patients were included in the study. A total of 46 nodules meeting the study criteria were examined. Measurements were performed on Apparent Diffusion Coefficient (ADC) maps of patients at two different b values (b 500 s/mm² and b 800 s/mm²), and the results were compared with histopathological findings.
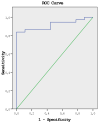
Results: Out of a total of 46 nodules, 37 were identified as benign, and 9 as malignant based on histopathological analysis. The mean ADC value at b 500 was lower in malignant nodules (1259.65 ± 328.13) compared to benign nodules (19037.48 ± 472.74). Similarly, the mean ADC value at b 800 was lower in malignant nodules (1081.72 ± 200.23) compared to benign nodules (1610.44 ± 418.06). When a cut-off value of 1.1 × 10- 3 was accepted for the differentiation of pathology, the sensitivity for distinguishing pathology with ADC values at b 500 was 83.3%, with a specificity of 90.0%, and for ADC values at b 800, the sensitivity was 71.4%, with a specificity of 89.7%.
Conclusion: DW-MRI without the need for contrast agent administration is a useful method in the differentiation of benign-malignant thyroid nodules.
Keywords: Apparent diffusion coefficient; B values; Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging; Thyroid nodule.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Role of apparent diffusion coefficient values and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in differentiation between benign and malignant thyroid nodules.Clin Imaging. 2012 Jan-Feb;36(1):1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2011.04.001. Clin Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22226435
-
[Application of nuclear magnetic dispersion weighted imaging and apparent diffusion coefficient in the identification of benign].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Apr;33(4):342-346. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2019.04.013. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 30970406 Chinese.
-
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging and ADC Mapping in Differentiating Benign from Malignant Thyroid Nodules.J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015 Nov;25(11):785-8. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2015. PMID: 26577961
-
Differentiation between benign and malignant thyroid nodules using diffusion-weighted imaging, a 3-T MRI study.Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2018 Oct-Dec;28(4):460-464. doi: 10.4103/ijri.IJRI_488_17. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2018. PMID: 30662211 Free PMC article.
-
T1 mapping and reduced field-of-view DWI at 3.0 T MRI for differentiation of thyroid papillary carcinoma from nodular goiter.Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2023 May;43(3):137-145. doi: 10.1111/cpf.12803. Epub 2022 Dec 3. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2023. PMID: 36440541 Review.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Accuracy of Diffusion-Weighted MRI for Differentiating Benign and Malignant Thyroid Nodules: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Cancers (Basel). 2025 Aug 18;17(16):2677. doi: 10.3390/cancers17162677. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40867306 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frates MC, Benson CB, Charboneau JW, Cibas ES, Clark OH, Coleman BG, Cronan JJ, Doubilet PM, Evans DB, Goellner JR, et al. Management of thyroid nodules detected at US: society of radiologists in ultrasound consensus conference statement. Radiology. 2005;237:794–800. 10.1148/radiol.2373050220. - PubMed
-
- Sisik A, Basak F, Kose E. Current approach to thyroid nodules: review of ATA 2015 and AACE/ACE/AME 2016 guidelines. Archives Clin Experimental Med. 2017;2:18–23. 10.25000/acem.303852).
-
- Gharib H, Papini E, Garber JR, Duick DS, Harrell RM, Hegedus L, Paschke R, Valcavi R, Vitti P. American association of clinical endocrinologists, American college of endocrinology, and associazione medici endocrinologi medical guidelines for clinical practice for the diagnosis and management of thyroid nodules-2016 update appendix. Endocr Pract. 2016;22:1–60. 10.4158/EP161208.GL). - PubMed
-
- Alvarado-Santiago M, Alvarez-Valentin D, Ruiz-Bermudez O, Gonzalez-Sepulveda L, Allende-Vigo M, Santiago-Rodriguez E, Rivas-Tunmanyan S. Fine-needle thyroid aspiration biopsy: clinical experience at the endocrinology clinics of the University Hospital of Puerto Rico. P R Health Sci J. 2017;36:5–10. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

