Treatment of Mid-Face Aging with Calcium Hydroxylapatite: Focus on Retaining Ligament Support
- PMID: 39552610
- PMCID: PMC11566585
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S468447
Treatment of Mid-Face Aging with Calcium Hydroxylapatite: Focus on Retaining Ligament Support
Abstract
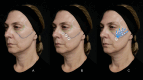
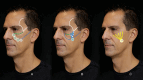
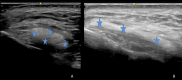
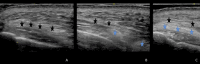
The mid-face has been rendered as the cornerstone of facial aesthetic improvement, since treating the mid-face has also beneficial effects on neighboring esthetic units and therefore should be one of the first areas to be assessed. Retaining ligaments (RL) bind soft tissue layers of the face to the underlying facial skeleton. It remains controversial whether RL suffers laxity with aging or if changes in 42 bone and other structures where ligaments are inserted lead to altered mechanical function of the latter. Enhancement of the supportive effect of the ligaments could help restore the soft tissues to their original anatomical positions and achieve a lifting effect. While injectable hyaluronic acid implants have been used to improve ligament support, calcium hydroxylapatite has one of the highest viscoelasticities when compared with other dermal fillers and can induce collagen synthesis, which could provide long-term laxity correction. In this preliminary report of a case series, our goal was to describe the use of calcium hydroxylapatite in different dilutions and combinations for different aging profiles to treat the midface as an alternative for hyaluronic acid injections and to describe the ultrasonographic behavior in the long run.
Keywords: aging pattern; calcium hydroxylapatite; hyaluronic acid; rejuvenation; retaining ligaments; soft tissue repositioning.
© 2024 Sato et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr Sato and Dr Muniz have been speakers for Merz Pharmaceuticals. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures



References
-
- Baker S, Neil A. Local Flaps in Facial Reconstruction, St. Louis. MO: Mosby; 2007:340.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

