Measuring brain perfusion by CT or MR as ancillary tests for diagnosis of brain death: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 39552613
- PMCID: PMC11568350
- DOI: 10.1093/bjro/tzae037
Measuring brain perfusion by CT or MR as ancillary tests for diagnosis of brain death: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: To gather and synthesize evidence regarding diagnostic accuracy of perfusion imaging by CT (CTP) or MR (MRP) for brain death (BD) diagnosis.
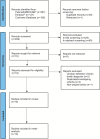
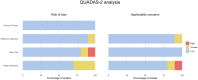
Methods: A systematic review and meta-analysis was prospectively registered with PROSPERO (CRD42022336353) and conducted in accordance with the PRISMA guidelines and independently by 3 reviewers. PubMed/MEDLINE, EMBASE and Cochrane Database were searched for relevant studies. Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies-2 was used to assess studies' quality. Meta-analysis was performed using univariate random-effects models.
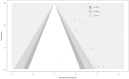
Results: Ten studies (328 patients) were included. Perfusion imaging (most commonly CTP, n = 8 studies) demonstrated a high sensitivity of 96.1% (95% CI, 89.5-98.6) for BD, consistent in subgroup analysis at 95.5% (95% CI, 86.5-98.6). Unfortunately, it was not feasible to calculate other metrics. Additionally, evidence of publication bias was identified in our findings.
Conclusions: The sensitivity of CTP or MRP for BD diagnosis is very high, comparable to CTA and TCD. However, considering most studies were retrospective, and lacked control groups and unambiguous criteria for perfusion imaging in BD assessment, results should be interpreted with caution. Future studies, ideally prospective, multi-centre, and with control groups are of utmost importance for validation of these methods, particularly with standardized technical parameters.
Advances in knowledge: Cerebral perfusion imaging using CT or MRI demonstrates high sensitivity in diagnosing BD, on par with CTA and TCD. Recommended by the World Brain Death group, this method holds promise for further investigation in this area.
Prospero registration number: CRD42022336353.
Keywords: CT; MR; arterial spin labelling; brain death; perfusion.
© The Author(s) 2024. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Institute of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

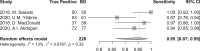
Similar articles
-
Implementation of Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA) and Computed Tomography Perfusion (CTP) in Polish Guidelines for Determination of Cerebral Circulatory Arrest (CCA) during Brain Death/Death by Neurological Criteria (BD/DNC) Diagnosis Procedure.J Clin Med. 2021 Sep 18;10(18):4237. doi: 10.3390/jcm10184237. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34575352 Free PMC article.
-
Computed tomography angiography as a confirmatory test for the diagnosis of brain death.J Neurosurg. 2018 Feb;128(2):639-644. doi: 10.3171/2016.10.JNS161042. Epub 2017 Mar 17. J Neurosurg. 2018. PMID: 28304181
-
Dynamic susceptibility MR perfusion in diagnosing recurrent brain metastases after radiotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Feb;51(2):524-534. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26812. Epub 2019 May 31. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31150144 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of Computed Tomographic Perfusion in Diagnosis of Brain Death: A Prospective Cohort Study.Med Sci Monit. 2018 May 4;24:2777-2785. doi: 10.12659/MSM.906304. Med Sci Monit. 2018. PMID: 29727439 Free PMC article.
-
Anatomical and Functional Computed Tomography for Diagnosing Hemodynamically Significant Coronary Artery Disease: A Meta-Analysis.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Jul;12(7 Pt 2):1316-1325. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.07.022. Epub 2018 Sep 12. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 30219398
References
-
- Bohatyrewicz R, Pastuszka J, Walas W, et al.Implementation of computed tomography angiography (CTA) and computed tomography perfusion (CTP) in Polish guidelines for determination of cerebral circulatory arrest (CCA) during brain death/death by neurological criteria (BD/DNC) diagnosis procedure. J Clin Med. 2021;10(18):4237. 10.3390/jcm10184237 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

