BDNF methylation associated with stress in women: Novel insights in epigenetics and inflammation
- PMID: 39552782
- PMCID: PMC11565430
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100900
BDNF methylation associated with stress in women: Novel insights in epigenetics and inflammation
Abstract
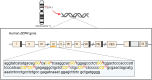
The brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene plays an important role in modulating the stress-response axis and inflammation, which can be regulated by epigenetic mechanisms. BNDF methylation has been associated with stress-related psychiatric disorders such as depression, anxiety and post-traumatic stress. Previous studies have reported that stressful events are involved with long-lasting alterations in DNA methylation (DNAm) of the BNDF exon IV promoter, suggesting that glucocorticoids and inflammatory cytokines can regulate this process. We previously found that perceived psychological stress is modulated by inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8 and IL-10, and IL-12p70, suggesting their role in mediating the stress response. However, the epigenetic mechanism mediating this response has yet to be fully understood. In this study, we propose that high perceived stress and high serum levels of inflammatory cytokines may correlate with specific methylation sites within the BNDF exon IV promoter. To address these questions, we conducted a cross-sectional study of 82 adult women teachers working in basic education in Brazil. The perceived stress scale was used to assess stress and blood samples were collected for the measurement of inflammatory markers and BNDF methylation through flow cytometry assay and DNA pyrosequencing, respectively. We detected differentially methylated CpG sites in the BNDF gene, where 5 CpG sites were directly correlated with high stress levels. However, 4 CpG sites showed inverse effects, indicating that changes in methylation levels in those sites could lead to a protective effect on perceived stress. About inflammatory markers, IL-6 and IL-8 were associated with high perceived stress. However, only IL-8 and IL-10 showed simultaneous modulation of perceived stress, while IL-10 and IL12p70 correlated with DNAm. We found that higher levels in IL-10 and IL-12p70 serum decrease methylation in CpG11. A direct relationship was also found to IL-12p70, where higher levels in serum increase methylation in CpG5 and 13, respectively. Taken as a whole, our findings reinforce the hypothesis regarding stress-sensitive regions within the BDNF gene, mainly for CpG5, 11, and 13. In addition to these results, CpG7 and 9 may be regarded as stress-protective regions. Our data suggest that BDNF DNAm in the blood may represent a novel biomarker for early detection of adverse effects of chronic exposure to stress in healthy individuals.
Keywords: BDNF DNA methylation; Healthy; Inflammatory cytokines; Stress.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this article.
Figures

References
-
- Alece Arantes Moreno I., Rodrigues de Oliveira D., Ribeiro Borçoi A., Fungaro Rissatti L., Vitorino Freitas F., Arantes L.M.R.B., Oliveira Mendes S., dos Santos Vieira T., Risse Quaioto B., Cerbino Doblas P. Methylation of BDNF gene in association with episodic memory in women. Front. Neurosci. 2023;17 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alivizatou A.-M., Psarropoulou C. vol. 1. STUDENT INTERNATIONAL BIOLOGICAL & BIOMEDICAL RESEARCH; 2024. (Effects of Estrogen on Brain and Cognitive Senescence).
-
- Au A., Feher A., McPhee L., Jessa A., Oh S., Einstein G. Estrogens, inflammation and cognition. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 2016;40:87–100. - PubMed
-
- Beal S.L. Ways to fit a PK model with some data below the quantification limit. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2001;28:481–504. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

