TNFα-reliant FSP1 up-regulation promotes intervertebral disc degeneration via caspase 3-dependent apoptosis
- PMID: 39552786
- PMCID: PMC11565395
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101251
TNFα-reliant FSP1 up-regulation promotes intervertebral disc degeneration via caspase 3-dependent apoptosis
Abstract
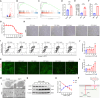
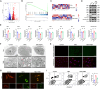
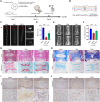
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is a common chronic inflammatory degenerative disease that causes lower back pain. However, the underlying mechanisms of IDD remain unclear. Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1 (FSP1) is a newly identified suppressor for ferroptosis. This study aims to investigate the role of FSP1 in IDD. Nucleus pulposus (NP) tissues in humans were collected and NP cells from rats were isolated to detect FSP1 expression pattern. The relationship between FSP1-mediated ferroptosis and apoptosis was identified using FSP1 inhibitor iFSP1. RNA sequencing was utilized to seek downstream molecules and related signaling pathways. Moreover, both exogenous recombinant FSP1 protein and endogenous small interfering RNA were implemented in this study to clarify the role of FSP1 in tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα)-mediated NP cell apoptosis. Ultimately, the underlying mechanisms of FSP1-related signaling pathway in IDD were uncovered both in vitro and in vivo. As a result, FSP1 was up-regulated in human degenerative NP tissues and after TNFα stimulation. FSP1 inhibition by iFSP1 fails to trigger ferroptosis in NP cells while inhibiting TNFα-mediated apoptosis. Further experiments demonstrated that FSP1 was closely related to TNFα-reliant caspase 3 activation and mitochondrial damage. However, the exogenous addition of recombinant protein FSP1 does not induce cell death or intensify the efficacy of TNFα. Mechanically, FSP1 is involved in TNFα-mediated NF-κB signaling activation to accelerate the development of IDD. This study demonstrated that FSP1 promotes IDD through TNFα-reliant NF-κB signaling activation and caspase 3-dependent apoptosis. These findings suggested a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of IDD.
Keywords: Caspase 3; FSP1; Intervertebraldisc degeneration; NF-κB; TNFα; iFSP1.
© 2024 The Authors. Publishing services by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of KeAi Communications Co., Ltd.
Figures





References
-
- Vlaeyen J.W.S., Maher C.G., Wiech K., et al. Low back pain. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2018;4(1):52. - PubMed
-
- Knezevic N.N., Candido K.D., Vlaeyen J.W.S., Van Zundert J., Cohen S.P. Low back pain. Lancet. 2021;398(10294):78–92. - PubMed
-
- Hoy D., March L., Brooks P., et al. The global burden of low back pain: estimates from the Global Burden of Disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(6):968–974. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

