Tracheobronchial Amyloidosis Causing Left Lung Collapse: A Case Report
- PMID: 39553128
- PMCID: PMC11567755
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.71658
Tracheobronchial Amyloidosis Causing Left Lung Collapse: A Case Report
Abstract
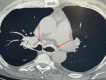
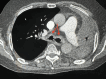
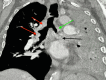
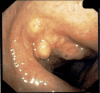
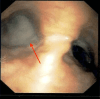
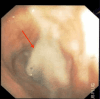
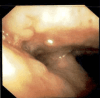
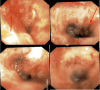
Tracheobronchial amyloidosis is a rare condition characterized by the deposition of amyloid proteins in the trachea and bronchi, leading to significant respiratory symptoms such as chronic mucoid, cough, dyspnea, and recurrent respiratory infections. We present the case of a 61-year-old individual who developed tracheobronchial amyloidosis, which poses a diagnostic challenge due to its clinical and radiological resemblance to other pulmonary disorders, including chronic bronchitis. Histologically, tracheobronchial amyloidosis is characterized by the presence of amyloid deposits confirmed by Congo red staining, which shows apple-green birefringence under polarized light. Further confirmation can be obtained through electron microscopy, revealing non-branching fibrils. This report explores the clinical presentation, diagnostic challenges, and management of tracheobronchial amyloidosis. Therapeutic interventions may include bronchoscopic procedures to remove obstructive amyloid deposits and systemic treatments such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy to address the underlying amyloid process, aiming to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Keywords: amyloid mass; amyloid plaque; amyloidosis; bronchoscopy; chronic bronchitis; congo red stain; lung collapse; tracheobronchial.
Copyright © 2024, Karimi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Human subjects: Consent was obtained or waived by all participants in this study. Conflicts of interest: In compliance with the ICMJE uniform disclosure form, all authors declare the following: Payment/services info: All authors have declared that no financial support was received from any organization for the submitted work. Financial relationships: All authors have declared that they have no financial relationships at present or within the previous three years with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work. Other relationships: All authors have declared that there are no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures


References
-
- Bustamante JG, Zaidi SR. StatPearls [Internet] Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024. Amyloidosis. - PubMed
-
- Cytochemistry of brain amyloid in adult dementia. Torack RM, Lynch RG. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;53:189–196. - PubMed
-
- Pulmonary and tracheobronchial amyloidosis. Berk JL, O'Regan A, Skinner M. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;23:155–165. - PubMed
-
- Amyloidosis: diagnosis and new therapies for a misunderstood and misdiagnosed disease. Thomas VE, Smith J, Benson MD, Dasgupta NR. Neurodegener Dis Manag. 2019;9:289–299. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
