Evodiamine exerts anti-cancer activity including growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis induction in human follicular thyroid cancers
- PMID: 39553211
- PMCID: PMC11560817
- DOI: 10.62347/DNTG2917
Evodiamine exerts anti-cancer activity including growth inhibition, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis induction in human follicular thyroid cancers
Abstract
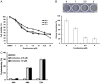
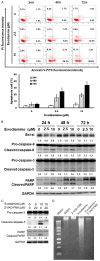
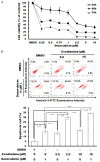
Thyroid cancer (TC) is one of the most prevalent endocrine malignancy with a steadily increasing incidence globally. Although standard treatments like thyroidectomy and radioiodine therapy effectively manage most cases of differentiated thyroid cancers (DTC), certain recurrent cases or those involving poorly differentiated thyroid cancers (PDTC) demand more specialized interventions. Follicular thyroid cancer (FTC) is the second most common type of DTC, and frequently metastasizes through the bloodstream to distant sites such as bones and lungs which is a leading cause of metastatic and recurrent DTC and significantly affects survival. However, existing drugs primarily address symptom management without offering a curative solution. Therefore, it is urgent to develop a new therapeutic agent for these challenging cases. Evodiamine (EVO), extracted from Evodia rutaecarpa, has shown potential as an anti-cancer agent in multiple types of human cancers including anaplastic thyroid cancer (ATC) and papillary thyroid cancer (PTC) cells. However, the anti-cancer effects of EVO on FTC have remained unclear. Therefore, the present study aims to investigate the anti-cancer effects of EVO in FTC cells. Our data showed that EVO effectively inhibits FTC cell growth, induces cell cycle arrest, and triggers apoptosis. Additionally, our study explored the underlying mechanisms through which EVO affects signaling pathways. To verify the anti-cancer effects of combination chemotherapy, EVO and doxorubicin were used together in FTC cells. In conclusion, this study demonstrates that EVO shows significant anti-human FTC activity, making it a promising therapeutic candidate for the treatment of follicular thyroid cancers.
Keywords: Evodiamine; anti-cancer therapy; apoptosis; follicular thyroid cancer.
AJCR Copyright © 2024.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
