Improving understanding of ferroptosis: Molecular mechanisms, connection with cellular senescence and implications for aging
- PMID: 39553553
- PMCID: PMC11564042
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39684
Improving understanding of ferroptosis: Molecular mechanisms, connection with cellular senescence and implications for aging
Abstract
In the face of cell damage, cells can initiate a response ranging from survival to death, the balance being crucial for tissue homeostasis and overall health. Cell death, in both accidental and regulated forms, plays a fundamental role in maintaining tissue homeostasis. Among the regulated mechanisms of cell death, ferroptosis has garnered attention for its iron-dependent phospholipid (PL) peroxidation and its implications in aging and age-related disorders, as well as for its therapeutic relevance. In this review, we provide an overview of the mechanisms, regulation, and physiological and pathological roles of ferroptosis. We present new insights into the relationship between ferroptosis, cellular senescence and aging, emphasizing how alterations in ferroptosis pathways contribute to aging-related tissue dysfunction. In addition, we examine the therapeutic potential of ferroptosis in aging-related diseases, offering innovative insights into future interventions aimed at mitigating the effects of aging and promoting longevity.
Keywords: Aging-related diseases; Ferroptosis; Iron metabolism aging; Phospholipid (PL) peroxidation; Redox homeostasis.
© 2024 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
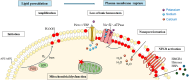
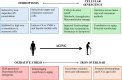

References
-
- Galluzzi L., Vitale I., Aaronson S.A., Abrams J.M., Adam D., Agostinis P., Alnemri E.S., Altucci L., Amelio I., Andrews D.W., Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M., Antonov A.V., Arama E., Baehrecke E.H., Barlev N.A., Bazan N.G., Bernassola F., Bertrand M.J.M., Bianchi K., Blagosklonny M.V., Blomgren K., Borner C., Boya P., Brenner C., Campanella M., Candi E., Carmona-Gutierrez D., Cecconi F., Chan F.K.M., Chandel N.S., Cheng E.H., Chipuk J.E., Cidlowski J.A., Ciechanover A., Cohen G.M., Conrad M., Cubillos-Ruiz J.R., Czabotar P.E., D'Angiolella V., Dawson T.M., Dawson V.L., De Laurenzi V., De Maria R., Debatin K.M., Deberardinis R.J., Deshmukh M., Di Daniele N., Di Virgilio F., Dixit V.M., Dixon S.J., Duckett C.S., Dynlacht B.D., El-Deiry W.S., Elrod J.W., Fimia G.M., Fulda S., García-Sáez A.J., Garg A.D., Garrido C., Gavathiotis E., Golstein P., Gottlieb E., Green D.R., Greene L.A., Gronemeyer H., Gross A., Hajnoczky G., Hardwick J.M., Harris I.S., Hengartner M.O., Hetz C., Ichijo H., Jäättelä M., Joseph B., Jost P.J., Juin P.P., Kaiser W.J., Karin M., Kaufmann T., Kepp O., Kimchi A., Kitsis R.N., Klionsky D.J., Knight R.A., Kumar S., Lee S.W., Lemasters J.J., Levine B., Linkermann A., Lipton S.A., Lockshin R.A., López-Otín C., Lowe S.W., Luedde T., Lugli E., MacFarlane M., Madeo F., Malewicz M., Malorni W., Manic G., Marine J.C., Martin S.J., Martinou J.C., Medema J.P., Mehlen P., Meier P., Melino S., Miao E.A., Molkentin J.D., Moll U.M., Muñoz-Pinedo C., Nagata S., Nuñez G., Oberst A., Oren M., Overholtzer M., Pagano M., Panaretakis T., Pasparakis M., Penninger J.M., Pereira D.M., Pervaiz S., Peter M.E., Piacentini M., Pinton P., Prehn J.H.M., Puthalakath H., Rabinovich G.A., Rehm M., Rizzuto R., Rodrigues C.M.P., Rubinsztein D.C., Rudel T., Ryan K.M., Sayan E., Scorrano L., Shao F., Shi Y., Silke J., Simon H.U., Sistigu A., Stockwell B.R., Strasser A., Szabadkai G., Tait S.W.G., Tang D., Tavernarakis N., Thorburn A., Tsujimoto Y., Turk B., Vanden Berghe T., Vandenabeele P., Vander Heiden M.G., Villunger A., Virgin H.W., Vousden K.H., Vucic D., Wagner E.F., Walczak H., Wallach D., Wang Y., Wells J.A., Wood W., Yuan J., Zakeri Z., Zhivotovsky B., Zitvogel L., Melino G., Kroemer G. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the nomenclature committee on cell death 2018. Cell Death Differ. 2018;25:486–541. doi: 10.1038/s41418-017-0012-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

